You may know of Erik Larson from his excellent book on the 1893 World’s Fair, The Devil in the White City. Larson’s In the Garden of Beasts: Love, Terror, and an American Family in Hitler’s Berlin was published in 2011 and tells the story of William Dodd, America’s first ambassador to Nazi Germany, roughly from the time of his appointment in 1933 to the events of the Night of the Long Knives, the July 1934 purge that consolidated Adolf Hitler’s power.
Reading it, I couldn’t help but notice several parallels between what was happening in 1933 & 1934 as Hitler worked to establish an authoritarian government in Germany and some of the actions of our current government and its President here in the US. If you think that sort of statement is hyperbolic, I urge you to read on and remember that there was a time when Nazi Germany and its rulers seemed to its citizenry and to the world to be, sure, a little extreme in their methods, fiery in their rhetoric, and engaged in some small actions against certain groups of people, but ultimately harmless…until they weren’t and then it was too late to do anything.
Here’s everything I highlighted on my Kindle presented with some light commentary…much of it speaks for itself and the parallels are obvious. I apologize (slightly) for the length, but this book provided a very interesting look at the Nazi regime before they became the world’s canonical example of evil.
Page 19 (The practiced good cop/bad cop of the tyrant.):
And Hitler himself had begun to seem like a more temperate actor than might have been predicted given the violence that had swept Germany earlier in the year. On May 10, 1933, the Nazi Party burned unwelcome books — Einstein, Freud, the brothers Mann, and many others — in great pyres throughout Germany, but seven days later Hitler declared himself committed to peace and went so far as to pledge complete disarmament if other countries followed suit. The world swooned with relief.
Page 28 (There is much in the book about anti-Semitic attitudes in the US in the 1930s and the indifference to what was happening to the Jews in Germany.):
But Roosevelt understood that the political costs of any public condemnation of Nazi persecution or any obvious effort to ease the entry of Jews into America were likely to be immense, because American political discourse had framed the Jewish problem as an immigration problem. Germany’s persecution of Jews raised the specter of a vast influx of Jewish refugees at a time when America was reeling from the Depression. The isolationists added another dimension to the debate by insisting, as did Hitler’s government, that Nazi oppression of Germany’s Jews was a domestic German affair and thus none of America’s business.
Page 29 (After reading the book, I couldn’t help but think that if Japan had not bombed Pearl Harbor in late 1941, the US might not have entered the war against Germany and may have gone down an isolationist path that led towards fascism.):
Indeed, anti-immigration sentiment in America would remain strong into 1938, when a Fortune poll reported that some two-thirds of those surveyed favored keeping refugees out of the country.
Page 38:
When the conversation turned to Germany’s persecution of Jews, Colonel House urged Dodd to do all he could “to ameliorate Jewish sufferings” but added a caveat: “the Jews should not be allowed to dominate economic or intellectual life in Berlin as they have done for a long time. “In this, Colonel House expressed a sentiment pervasive in America, that Germany’s Jews were at least partly responsible for their own troubles.
Page 40 (This is in reference to Dodd’s daughter Martha, who was 24 when he was named ambassador and accompanied him to Berlin.):
She knew little of international politics and by her own admission did not appreciate the gravity of what was occurring in Germany. She saw Hitler as “a clown who looked like Charlie Chaplin.” Like many others in America at this time and elsewhere in the world, she could not imagine him lasting very long or being taken seriously.
Page 41:
In this she reflected the attitude of a surprising proportion of other Americans, as captured in the 1930s by practitioners of the then-emerging art of public-opinion polling. One poll found that 41 percent of those contacted believed Jews had “too much power in the United States”; another found that one-fifth wanted to “drive Jews out of the United States.” (A poll taken decades in the future, in 2009, would find that the total of Americans who believed Jews had too much power had shrunk to 13 percent.)
Page 54 (The “if it’s not happening to me, it must not be happening” response to injustice.):
When Martha left her hotel she witnessed no violence, saw no one cowering in fear, felt no oppression. The city was a delight.
Page 56 (Read more about Coordination):
Beneath the surface, however, Germany had undergone a rapid and sweeping revolution that reached deep into the fabric of daily life. It had occurred quietly and largely out of easy view. At its core was a government campaign called Gleichschaltung — meaning “Coordination” — to bring citizens, government ministries, universities, and cultural and social institutions in line with National Socialist beliefs and attitudes.
Page 56 (This paragraph, and the one that follows below, about “self-coordination” was one of the most chilling I read…I had to put the book down for a bit after this.):
“Coordination” occurred with astonishing speed, even in sectors of life not directly targeted by specific laws, as Germans willingly placed themselves under the sway of Nazi rule, a phenomenon that became known as Selbstgleichschaltung, or “self-coordination.” Change came to Germany so quickly and across such a wide front that German citizens who left the country for business or travel returned to find everything around them altered, as if they were characters in a horror movie who come back to find that people who once were their friends, clients, patients, and customers have become different in ways hard to discern.
Page 57:
The Gestapo’s reputation for omniscience and malevolence arose from a confluence of two phenomena: first, a political climate in which merely criticizing the government could get one arrested, and second, the existence of a populace eager not just to step in line and become coordinated but also to use Nazi sensitivities to satisfy individual needs and salve jealousies. One study of Nazi records found that of a sample of 213 denunciations, 37 percent arose not from heartfelt political belief but from private conflicts, with the trigger often breathtakingly trivial. In October 1933, for example, the clerk at a grocery store turned in a cranky customer who had stubbornly insisted on receiving three pfennigs in change. The clerk accused her of failure to pay taxes. Germans denounced one another with such gusto that senior Nazi officials urged the populace to be more discriminating as to what circumstances might justify a report to the police. Hitler himself acknowledged, in a remark to his minister of justice, “we are living at present in a sea of denunciations and human meanness.”
Page 58:
“Hardly anyone thought that the threats against the Jews were meant seriously,” wrote Carl Zuckmayer, a Jewish writer. “Even many Jews considered the savage anti-Semitic rantings of the Nazis merely a propaganda device, a line the Nazis would drop as soon as they won governmental power and were entrusted with public responsibilities.” Although a song popular among Storm Troopers bore the title “When Jewish Blood Spurts from My Knife,” by the time of the Dodds’ arrival violence against Jews had begun to wane. Incidents were sporadic, isolated. “It was easy to be reassured,” wrote historian John Dippel in a study of why many Jews decided to stay in Germany. “On the surface, much of daily life remained as it had been before Hitler came to power. Nazi attacks on the Jews were like summer thunderstorms that came and went quickly, leaving an eerie calm.”
Page 66 (LOL, a “moderate nationalist regime”):
Neurath saw himself as a sobering force in the government and believed he could help control Hitler and his party. As one peer put it, “He was trying to train the Nazis and turn them into really serviceable partners in a moderate nationalist regime.”
Page 68:
It was a problem Messersmith had noticed time and again. Those who lived in Germany and who paid attention understood that something fundamental had changed and that a darkness had settled over the landscape. Visitors failed to see it.
Page 81:
Dodd reinterated his commitment to objectivity and understanding in an August 12 letter to Roosevelt, in which he wrote that while he did not approve of Germany’s treatment of Jews or Hitler’s drive to restore the country’s military power, “fundamentally, I believe a people has a right to govern itself and that other peoples must exercise patience even when cruelties and injustices are done. Give men a chance to try their schemes.”
Page 84 (Yeah, where did all those nice houses come from?):
The Dodds found many properties to choose from, though at first they failed to ask themselves why so many grand old mansions were available for lease so fully and luxuriously furnished, with ornate tables and chairs, gleaming pianos, and rare vases, maps, and books still in place.
Page 85 (Dodd’s Jewish landlord, who lived in the attic, rented his house to Dodd at a significant discount to gain protection from state persecution of Jews.):
Panofsky was sufficiently wealthy that he did not need the income from the lease, but he had seen enough since Hitler’s appointment as chancellor to know that no Jew, no matter how prominent, was safe from Nazi persecution. He offered 27a to the new ambassador with the express intention of gaining for himself and his mother an enhanced level of physical protection, calculating that surely even the Storm Troopers would not risk the international outcry likely to arise from an attack on the house shared by the American ambassador.
Page 94 (Nazi forces would often beat people who failed to “Heil Hitler!”, even non-Germans. This order did not stop the beatings.):
The next day, Saturday, August 19, a senior government official notified Vice Consul Raymond Geist that an order had been issued to the SA and SS stating that foreigners were not expected to give or return the Hitler salute.
Page 97:
She too had been shaken by the episode, but she did not let it tarnish her overall view of the country and the revival of spirit caused by the Nazi revolution. “I tried in a self-conscious way to justify the action of the Nazis, to insist that we should not condemn without knowing the whole story.”
Page 105:
Messersmith met with Dodd and asked whether the time had come for the State Department to issue a definitive warning against travel in Germany. Such a warning, both men knew, would have a devastating effect on Nazi prestige. Dodd favored restraint. From the perspective of his role as ambassador, he found these attacks more nuisance than dire emergency and in fact tried whenever possible to limit press attention.
Page 108:
Göring too seemed a relatively benign character, at least as compared with Hitler. Sigrid Schultz found him the most tolerable of the senior Nazis because at least “you felt you could be in the same room with the man,” whereas Hitler, she said, “kind of turned my stomach.” One of the American embassy’s officers, John C. White, said years later, “I was always rather favorably impressed by Göring. … If any Nazi was likeable, I suppose he came nearest to it.”
Page 115:
Martha’s love life took a dark turn when she was introduced to Rudolf Diels, the young chief of the Gestapo. He moved with ease and confidence, yet unlike Putzi Hanfstaengl, who invaded a room, he entered unobtrusively, seeping in like a malevolent fog.
Page 117:
Yet under Diels the Gestapo played a complex role. In the weeks following Hitler’s appointment as chancellor, Diels’s Gestapo acted as a curb against a wave of violence by the SA, during which Storm Troopers dragged thousands of victims to their makeshift prisons. Diels led raids to close them and found prisoners in appalling conditions, beaten and garishly bruised, limbs broken, near starvation, “like a mass of inanimate clay,” he wrote, “absurd puppets with lifeless eyes, burning with fever, their bodies sagging.”
Page 118:
During a gathering of foreign correspondents at Putzi Hanfstaengl’s home, Diels told the reporters, “The value of the SA and the SS, seen from my viewpoint of inspector-general responsible for the suppression of subversive tendencies and activities, lies in the fact that they spread terror. That is a wholesome thing.”
Page 130 (“When someone shows you who they are, believe them the first time.” -Maya Angelou):
Dodd said, “You cannot expect world opinion of your conduct to moderate so long as eminent leaders like Hitler and Goebbels announce from platforms, as in Nuremberg, that all Jews must be wiped off the earth.”
Page 134 (“A kind of daily suspense” is definitely a tool in the political toolbox today. The news media practices this as well.):
Klemperer detected a certain “hysteria of language” in the new flood of decrees, alarms, and intimidation — “This perpetual threatening with the death penalty!” — and in strange, inexplicable episodes of paranoid excess, like the recent nationwide search. In all this Klemperer saw a deliberate effort to generate a kind of daily suspense, “copied from American cinema and thrillers,” that helped keep people in line. He also gauged it to be a manifestation of insecurity among those in power.
Page 135:
Persecution of Jews continued in ever more subtle and wide-ranging form as the process of Gleichschaltung advanced. In September the government established the Reich Chamber of Culture, under the control of Goebbels, to bring musicians, actors, painters, writers, reporters, and filmmakers into ideological and, especially, racial alignment. In early October the government enacted the Editorial Law, which banned Jews from employment by newspapers and publishers and was to take effect on January 1, 1934. No realm was too petty: The Ministry of Posts ruled that henceforth when trying to spell a word over the telephone a caller could no longer say “D as in David,” because “David” was a Jewish name. The caller had to use “Dora.” “Samuel” became “Siegfried.” And so forth.
Page 136 (George Messersmith was the head of the US Consulate in Germany from 1930 to 1934 and was one of the few people at the time who properly diagnosed the Nazi threat. In a 1933 letter to the US State Department, he called Hitler and his cronies “psychopathic cases” that would “ordinarily be receiving treatment somewhere”.):
Messersmith proposed that one solution might be “forcible intervention from the outside.” But he warned that such an action would have to come soon. “If there were intervention by other powers now, probably about half of the population would still look upon it as deliverance,” he wrote. “If it is delayed too long, such intervention might meet a practically united Germany.” One fact was certain, Messersmith believed: Germany now posed a real and grave threat to the world. He called it “the sore spot which may disturb our peace for years to come.”
Page 148 (On a speech Dodd gave in Berlin in October 1933 in front of an audience that included Joseph Goebbels.):
He gave the talk the innocuous title “Economic Nationalism.” By citing the rise and fall of Caesar and episodes from French, English, and U.S. history, Dodd sought to warn of the dangers “of arbitrary and minority” government without ever actually mentioning contemporary Germany. It was not the kind of thing a traditional diplomat might have undertaken, but Dodd saw it as simply fulfilling Roosevelt’s original mandate.
Page 149 (The reaction to Dodd’s speech):
“When the thing was over about every German present showed and expressed a kind of approval which revealed the thought: ‘You have said what all of us have been denied the right to say.’” An official of the Deutsche Bank called to express his own agreement. He told Dodd, “Silent, but anxious Germany, above all the business and University Germany, is entirely with you and most thankful that you are here and can say what we can not say.”
Page 154 (Hanfstaengl, a confidant of Hitler, tried to set up Hitler with Martha Dodd as a moderating influence.):
Putzi Hanfstaengl knew of Martha’s various romantic relationships, but by the fall of 1933 he had begun to imagine for her a new partner. Having come to feel that Hitler would be a much more reasonable leader if only he fell in love, Hanfstaengl appointed himself matchmaker.
Page 154 (Shocker that Hitler was controlling and abusive when it came to women.):
Hitler liked women, but more as stage decoration than as sources of intimacy and love. There had been talk of numerous liaisons, typically with women much younger than he — in one case a sixteen-year-old named Maria Reiter. One woman, Eva Braun, was twenty-three years his junior and had been an intermittent companion since 1929. So far, however, Hitler’s only all-consuming affair had been with his young niece, Geli Raubal. She was found shot to death in Hitler’s apartment, his revolver nearby. The most likely explanation was suicide, her means of escaping Hitler’s jealous and oppressive affection — his “clammy possessiveness, “as historian Ian Kershaw put it.
Page 157 (The banality of evil…):
Apart from his mustache and his eyes, the features of his face were indistinct and unimpressive, as if begun in clay but never fired. Recalling his first impression of Hitler, Hanfstaengl wrote, “Hitler looked like a suburban hairdresser on his day off.”
Page 159 (On Dodd’s meeting with Hitler):
Though the session had been difficult and strange, Dodd nonetheless left the chancellery feeling convinced that Hitler was sincere about wanting peace.
Page 159:
“We must keep in mind, I believe, that when Hitler says anything he for the moment convinces himself that it is true. He is basically sincere; but he is at the same time a fanatic.”
Page 161 (Martha Dodd met Hitler once briefly):
At this vantage, she wrote, the mustache “didn’t seem as ridiculous as it appeared in pictures — in fact, I scarcely noticed it.” What she did notice were his eyes. She had heard elsewhere that there was something piercing and intense about his gaze, and now, immediately, she understood. “Hitler’s eyes,” she wrote, “were startling and unforgettable — they seemed pale blue in color, were intense, unwavering, hypnotic.”
Page 165 (I didn’t highlight this, but at several points in the book, officials from the US and other countries acknowledged that they also had a “Jewish problem”, i.e. the Jews had too much power, money, and influence.):
Dodd believed that one artifact of past excess — “another curious hangover,” he told Phillips — was that his embassy had too many personnel, in particular, too many who were Jewish. “We have six or eight members of the ‘chosen race’ here who serve in most useful but conspicuous positions,” he wrote. Several were his best workers, he acknowledged, but he feared that their presence on his staff impaired the embassy’s relationship with Hitler’s government and thus impeded the day-to-day operation of the embassy.
Page 186 (Again with the belief that you can control an irrational & psychopathic nationalist.):
Papen was a protege of President Hindenburg, who affectionately called him Franzchen, or Little Franz. With Hindenburg in his camp, Papen and fellow intriguers had imagined they could control Hitler. “I have Hindenburg’s confidence,” Papen once crowed. “Within two months we will have pushed Hitler so far into a corner that he’ll squeak.” It was possibly the greatest miscalculation of the twentieth century. As historian John Wheeler-Bennett put it, “Not until they had riveted the fetters upon their own wrists did they realize who indeed was captive and who captor.”
Page 189 (Relevant to this are Hannah Arendt’s thoughts on lies. See also Donald Trump’s “fanciful thinking” about 9/11 and his continuing condemnation of the Central Park Five.):
An odd kind of fanciful thinking seemed to have bedazzled Germany, to the highest levels of government. Earlier in the year, for example, Göring had claimed with utter sobriety that three hundred German Americans had been murdered in front of Independence Hall in Philadelphia at the start of the past world war.
Page 213 (Subtle oppression is still oppression and sets the stage for the later acceptance of overt & violent oppression.):
But Schweitzer understood this was in large part an illusion. Overt violence against Jews did appear to have receded, but a more subtle oppression had settled in its place. “What our friend had failed to see from outward appearances is the tragedy that is befalling daily the job holders who are gradually losing their positions,” Schweitzer wrote. He gave the example of Berlin’s department stores, typically owned and staffed by Jews. “While on the one hand one can observe a Jewish department store crowded as usual with non-Jews and Jews alike, one can observe in the very next department store the total absence of a single Jewish employee.”
Page 223 (Even rumors are enough to change behavior when dealing with an authoritarian regime.):
A common story had begun to circulate: One man telephones another and in the course of their conversation happens to ask, “How is Uncle Adolf?” Soon afterward the secret police appear at his door and insist that he prove that he really does have an Uncle Adolf and that the question was not in fact a coded reference to Hitler. Germans grew reluctant to stay in communal ski lodges, fearing they might talk in their sleep. They postponed surgeries because of the lip-loosening effects of anesthetic.
Page 225:
You lingered at street corners a beat or two longer to see if the faces you saw at the last corner had now turned up at this one. In the most casual of circumstances you spoke carefully and paid attention to those around you in a way you never had before. Berliners came to practice what became known as “the German glance” — der deutsche Blick — a quick look in all directions when encountering a friend or acquaintance on the street.
Page 226:
An American professor who was a friend of the Dodds, Peter Olden, wrote to Dodd on January 30, 1934, to tell him he had received a message from his brother-in-law in Germany in which the man described a code he planned to use in all further correspondence. The word “rain,” in any context, would mean he had been placed in a concentration camp. The word “snow” would mean he was being tortured. “It seems absolutely unbelievable,” Olden told Dodd. “If you think that this is really something in the nature of a bad joke, I wonder if you could mention so in a letter to me.”
Page 229 (Hitler had been saying this shit since the 1920s and no one took him seriously.):
First Hitler spoke of broader matters. Germany, he declared, needed more room in which to expand, “more living space for our surplus population. “And Germany, he said, must be ready to take it. “The Western powers will never yield this vital space to us, “Hitler said.”That is why a series of decisive blows may become necessary - first in the West, and then in the East.”
Page 241 (A reminder that the US was also treating millions of people as second-class citizens at this time.):
After studying the resolution, Judge Moore concluded that it could only put Roosevelt “in an embarrassing position.” Moore explained: “If he declined to comply with the request, he would be subjected to considerable criticism. On the other hand, if he complied with it he would not only incur the resentment of the German Government, but might be involved in a very acrimonious discussion with that Government which conceivably might, for example, ask him to explain why the negroes of this country do not fully enjoy the right of suffrage; why the lynching of negroes in Senator Tydings’ State and other States is not prevented or severely punished; and how the anti-Semitic feeling in the United States, which unfortunately seems to be growing, is not checked.”
Page 265:
He reached into his pocket, and pulled out a small bag of candy fruit drops. Lutschbonbons. Bella had loved them as a child.” Have one,” Hanfstaengl said. “They are made especially for the Führer.” She chose one. Just before she popped it into her mouth she saw that it was embossed with a swastika. Even fruit drops had been “coordinated.”
Page 270 (Wow, “inner emigration”.):
In the months following Hitler’s ascension to chancellor, the German writers who were not outright Nazis had quickly divided into two camps — those who believed it was immoral to remain in Germany and those who felt the best strategy was to stay put, recede as much as possible from the world, and wait for the collapse of the Hitler regime. The latter approach became known as “inner emigration,” and was the path Fallada had chosen.
Page 273:
Even so, Fallada made more and more concessions, eventually allowing Goebbels to script the ending of his next novel, Iron Gustav, which depicted the hardships of life during the past world war. Fallada saw this as a prudent concession. “I do not like grand gestures,” he wrote; “being slaughtered before the tyrant’s throne, senselessly, to the benefit of no one and to the detriment of my children, that is not my way.” He recognized, however, that his various capitulations took a toll on his writing. He wrote to his mother that he was not satisfied with his work. “I cannot act as I want to — if I want to stay alive. And so a fool gives less than he has.” Other writers, in exile, watched with disdain as Fallada and his fellow inner emigrants surrendered to government tastes and demands. Thomas Mann, who lived abroad throughout the Hitler years, later wrote their epitaph: “It may be superstitious belief, but in my eyes, any books which could be printed at all in Germany between 1933 and 1945 are worse than worthless and not objects one wishes to touch. A stench of blood and shame attaches to them. They should all be pulped.”
Page 279 (Nazi leaders had already begun using their power to amass opulent wealth.):
“Ladies and gentlemen,” Göring said, “in a few minutes you will witness a unique display of nature at work.” He gestured toward an iron cage. “In this cage is a powerful male bison, an animal almost unheard of on the Continent. … He will meet here, before your very eyes, the female of his species. Please be quiet and don’t be afraid.” Göring’s keepers opened the cage. “Ivan the Terrible,” Göring commanded, “I order you to leave the cage.” The bull did not move. Göring repeated his command. Once again the bull ignored him. The keepers now attempted to prod Ivan into action. The photographers readied themselves for the lustful charge certain to ensue. Britain’s Ambassador Phipps wrote in his diary that the bull emerged from the cage “with the utmost reluctance, and, after eyeing the cows somewhat sadly, tried to return to it.” Phipps also described the affair in a later memorandum to London that became famous within the British foreign office as “the bison dispatch.”
Page 282:
The next day Phipps wrote about Göring’s open house in his diary. “The whole proceedings were so strange as at times to convey a feeling of unreality,” he wrote, but the episode had provided him a valuable if unsettling insight into the nature of Nazi rule. “The chief impression was that of the most pathetic naivete of General Göring, who showed us his toys like a big, fat, spoilt child: his primeval woods, his bison and birds, his shooting-box and lake and bathing beach, his blond ‘private secretary,’ his wife’s mausoleum and swans and sarsen stones. … And then I remembered there were other toys, less innocent though winged, and these might some day be launched on their murderous mission in the same childlike spirit and with the same childlike glee.”
Page 306 (during the aforementioned Night of the Long Knives purge):
In Munich, Hitler read through a list of the prisoners and marked an “X” next to six names. He ordered all six shot immediately. An SS squad did so, telling the men just before firing, “You have been condemned to death by the Führer! Heil Hitler.” The ever-obliging Rudolf Hess offered to shoot Röhm himself, but Hitler did not yet order his death. For the moment, even he found the idea of killing a longtime friend to be abhorrent.
Page 321 (in the aftermath of the purge):
As the weekend progressed, the Dodds learned that a new phrase was making the rounds in Berlin, to be deployed upon encountering a friend or acquaintance on the street, ideally with a sardonic lift of one eyebrow: “Lebst du noch?” Which meant, “Are you still among the living?”
Page 328:
Throughout that first year in Germany, Dodd had been struck again and again by the strange indifference to atrocity that had settled over the nation, the willingness of the populace and of the moderate elements in the government to accept each new oppressive decree, each new act of violence, without protest. It was as if he had entered the dark forest of a fairy tale where all the rules of right and wrong were upended.
Page 333:
Hitler’s purge would become known as “The Night of the Long Knives” and in time would be considered one of the most important episodes in his ascent, the first act in the great tragedy of appeasement. Initially, however, its significance was lost. No government recalled its ambassador or filed a protest; the populace did not rise in revulsion.
Page 334 (Hitler cracked down on the Storm Troopers because their leadership was against him, but their doing of bad deeds were soon replaced by the SS.):
The controlled press, not surprisingly, praised Hitler for his decisive behavior, and among the public his popularity soared. So weary had Germans become of the Storm Troopers’ intrusions in their lives that the purge seemed like a godsend. An intelligence report from the exiled Social Democrats found that many Germans were “extolling Hitler for his ruthless determination” and that many in the working class “have also become enslaved to the uncritical deification of Hitler.”
Page 336 (on the good treatment of horses in Germany):
“At a time when hundreds of men have been put to death without trial or any sort of evidence of guilt, and when the population literally trembles with fear, animals have rights guaranteed them which men and women cannot think of expecting.”
Page 340 (Dodd eventually came to see the danger of Nazi Germany):
He became one of the few voices in U.S. government to warn of the true ambitions of Hitler and the dangers of America’s isolationist stance. He told Secretary Hull in a letter dated August 30, 1934, “With Germany united as it has never before been, there is feverish arming and drilling of 1,500,000 men, all of whom are taught every day to believe that continental Europe must be subordinated to them.” He added, “I think we must abandon our so-called isolation.” He wrote to the army chief of staff, Douglas MacArthur, “In my judgment, the German authorities are preparing for a great continental struggle. There is ample evidence. It is only a question of time.”
Page 351:
Dodd’s sorrow and loneliness took a toll on his already fragile health, but still he pressed on and gave lectures around the country, in Texas, Kansas, Wisconsin, Illinois, Maryland, and Ohio, always reprising the same themes — that Hitler and Nazism posed a great risk to the world, that a European war was inevitable, and that once war began the United States would find it impossible to remain aloof. One lecture drew an audience of seven thousand people. In a June 10, 1938, speech in Boston, at the Harvard Club — that den of privilege — Dodd talked of Hitler’s hatred of Jews and warned that his true intent was “to kill them all.”
Dodd died in February 1940. He lived long enough to witness the start of Hitler’s war on Europe but not long enough to see America’s isolationism come to an end or Hitler’s attempt to kill all the Jews.
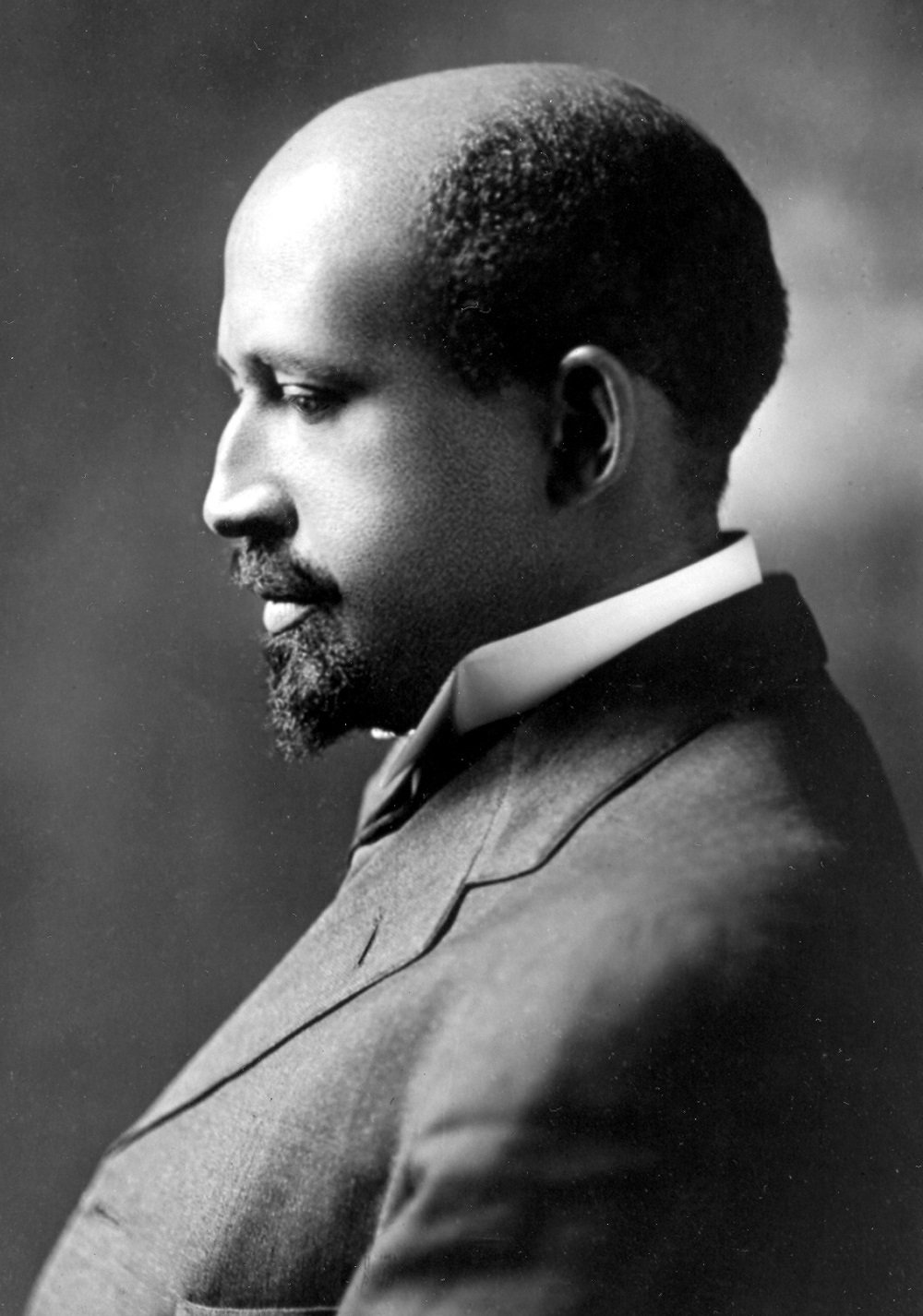

Tomorrow, February 23, is William Edward Burghardt Du Bois’s birthday. Du Bois was born in 1868 and died in 1963. In fact, Du Bois died, in Ghana, the day before the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom. Roy Wilkins and hundreds of thousands of marchers observed Du Bois’s death with a moment of silence.
Du Bois is one of the most influential and important thinkers in American history. He wrote many, many speeches, essays, and books that are essential to understanding American culture, society, labor, and politics, particularly as they affected and were affected in turn by black people.
My favorite Du Bois essay, and one of the first I ever read, was and probably still is “Criteria of Negro Art.” It was written and published in 1926, and first presented as a speech in honor of Carter Woodson. I have in the last few years met otherwise extremely well-read people who knew nothing of this essay and have since sworn an oath to remedy that wherever possible. So you get to read some excerpts from it now.
The Big Idea of the essay is really formulated in the fourth paragraph:
What do we want? What is the thing we are after? As it was phrased last night it had a certain truth: We want to be Americans, full-fledged Americans, with all the rights of other American citizens. But is that all? Do we want simply to be Americans? Once in a while through all of us there flashes some clairvoyance, some clear idea, of what America really is. We who are dark can see America in a way that white Americans cannot. And seeing our country thus, are we satisfied with its present goals and ideals?
The answer to this first question “What do we want?” is Art, the proper appreciation of Beauty and Freedom; and the answer to the last question, “are we satisfied with [America’s] present goals and ideals?” is, of course, No.
In the twelfth paragraph, Du Bois argues that the lives of black Americans, not just the emerging intellectual bourgeoisie of the 1920s, but the lives of all black Americans, for their entire history, are the proper subject of this new kind of Art:
This is brought to us peculiarly when as artists we face our own past as a people. There has come to us — and it has come especially through the man we are going to honor tonight — a realization of that past, of which for long years we have been ashamed, for which we have apologized. We thought nothing could come out of that past which we wanted to remember; which we wanted to hand down to our children. Suddenly, this same past is taking on form, color, and reality, and in a half shamefaced way we are beginning to be proud of it. We are remembering that the romance of the world did not die and lie forgotten in the Middle Age [sic]; that if you want romance to deal with you must have it here and now and in your own hands.
Du Bois, after all, was a sociologist, and knew how to mobilize facts and figures; he does so in this anecdote, about black soldiers who fought in the Great War:
Have you heard the story of the conquest of German East Africa? Listen to the untold tale: There were 40,000 black men and 4,000 white men who talked German. There were 20,000 black men and 12,000 white men who talked English. There were 10,000 black men and 400 white men who talked French. In Africa then where the Mountains of the Moon raised their white and snow-capped heads into the mouth of the tropic sun, where Nile and Congo rise and the Great Lakes swim, these men fought; they struggled on mountain, hill and valley, in river, lake and swamp, until in masses they sickened, crawled and died; until the 4,000 white Germans had become mostly bleached bones; until nearly all the 12,000 white Englishmen had returned to South Africa, and the 400 Frenchmen to Belgium and Heaven; all except a mere handful of the white men died; but thousands of black men from East, West and South Africa, from Nigeria and the Valley of the Nile, and from the West Indies still struggled, fought and died. For four years they fought and won and lost German East Africa; and all you hear about it is that England and Belgium conquered German Africa for the allies!
In the 18th paragraph, he demolishes the premise that the success of black artists in and of itself is evidence of racial progress as such:
With the growing recognition of Negro artists in spite of the severe handicaps, one comforting thing is occurring to both white and black. They are whispering, “Here is a way out. Here is the real solution of the color problem. The recognition accorded Cullen, Hughes, Fauset, White and others shows there is no real color line. Keep quiet! Don’t complain! Work! All will be well!”
And beginning in the 21st paragraph, he quickly, and with startling beauty, poses the real problem for black artists working in America:
There is in New York tonight a black woman molding clay by herself in a little bare room, because there is not a single school of sculpture in New York where she is welcome. Surely there are doors she might burst through, but when God makes a sculptor He does not always make the pushing sort of person who beats his way through doors thrust in his face. This girl is working her hands off to get out of this country so that she can get some sort of training.
There was Richard Brown. If he had been white he would have been alive today instead of dead of neglect. Many helped him when he asked but he was not the kind of boy that always asks. He was simply one who made colors sing.
There is a colored woman in Chicago who is a great musician. She thought she would like to study at Fontainebleau this summer where Walter Damrosch and a score of leaders of Art have an American school of music. But the application blank of this school says: “I am a white American and I apply for admission to the school.”
We can go on the stage; we can be just as funny as white Americans wish us to be; we can play all the sordid parts that America likes to assign to Negroes; but for any thing else there is still small place for us.
I first read this essay at least twenty years ago, but I swear I’ve thought about “when God makes a sculptor He does not always make the pushing sort of person who beats his way through doors thrust in his face” every day since. Every day. I think about it for black artists, for gay, lesbian, transgender, and queer artists, for women who put up with harassment and abuse from the very people who’ve promised to help them pursue their art. And I think about it even more when I think about the thousands if not millions of people who were turned away from ever becoming artists, writers, musicians, actors, sculptors, dancers, engineers, designers, programmers, or any other critical or creative field where doors are so often thrust in your face.
Yes, push through those doors. But hold them open after you. Because the next person, God may not have made to be one whose first inclination is to push.
All art, Du Bois argues, and in particular the art of black people, relies on not just Beauty, but Truth and Goodness, “goodness in all its aspects of justice, honor and right — not for sake of an ethical sanction but as the one true method of gaining sympathy and human interest.” Art that seeks to restore the balance of truth and goodness, on a subject like the lives of black people, which is prone to so much distortion and misunderstanding, necessarily relies on an ideal of Justice. This leads to maybe the most famous quote of the essay:
Thus all Art is propaganda and ever must be, despite the wailing of the purists. I stand in utter shamelessness and say that whatever art I have for writing has been used always for propaganda for gaining the right of black folk to love and enjoy. I do not care a damn for any art that is not used for propaganda. But I do care when propaganda is confined to one side while the other is stripped and silent.
What America is getting from its white artists, is propaganda that shames and distorts the lives of black people, in order to show them to be sinister and/or servile.
In other words, the white public today demands from its artists, literary and pictorial, racial pre-judgment which deliberately distorts Truth and Justice, as far as colored races are concerned, and it will pay for no other.
But respectability politics is almost as dangerous, when it comes to art.
On the other hand, the young and slowly growing black public still wants its prophets almost equally unfree. We are bound by all sorts of customs that have come down as second-hand soul clothes of white patrons. We are ashamed of sex and we lower our eyes when people will talk of it. Our religion holds us in superstition. Our worst side has been so shamelessly emphasized that we are denying we have or ever had a worst side. In all sorts of ways we are hemmed in and our new young artists have got to fight their way to freedom.
And here is the bind, the contradiction which even Du Bois cannot completely unravel. Until black artists produce great art, black people will not be registered by white people as fully human. And once those great artists appear, their blackness will be erased away, in favor of a false universality and sham humanism.
And then do you know what will be said? It is already saying. Just as soon as true Art emerges; just as soon as the black artist appears, someone touches the race on the shoulder and says, “He did that because he was an American, not because he was a Negro; he was born here; he was trained here; he is not a Negro — what is a Negro anyhow? He is just human; it is the kind of thing you ought to expect.”
I do not doubt that the ultimate art coming from black folk is going to be just as beautiful, and beautiful largely in the same ways, as the art that comes from white folk, or yellow, or red; but the point today is that until the art of the black folk compells [sic] recognition they will not be rated as human. And when through art they compell [sic] recognition then let the world discover if it will that their art is as new as it is old and as old as new.
Du Bois closes the essay with one of the most beautiful passages I’ve ever read. It’s also the most personal. It’s about his friend and classmate William Vaughan Moody.
I had a classmate once who did three beautiful things and died. One of them was a story of a folk who found fire and then went wandering in the gloom of night seeking again the stars they had once known and lost; suddenly out of blackness they looked up and there loomed the heavens; and what was it that they said? They raised a mighty cry: “It is the stars, it is the ancient stars, it is the young and everlasting stars!”
There are other great essays about the relationship between politics and art. Some of them are subtler than Du Bois’s. Some take on more directly the nature of politics or art itself. Some have a more politically radical intent. Some name more names, and pick more fights. But nobody but Du Bois, working with the economy he’s working with, states as directly the political problems facing art, artists, art critics, and the art-loving public. Nobody gets to the root of things as squarely as he does.
It’s the best essay on art and politics ever written. And if you don’t agree, I want to see your candidate. That’s all.
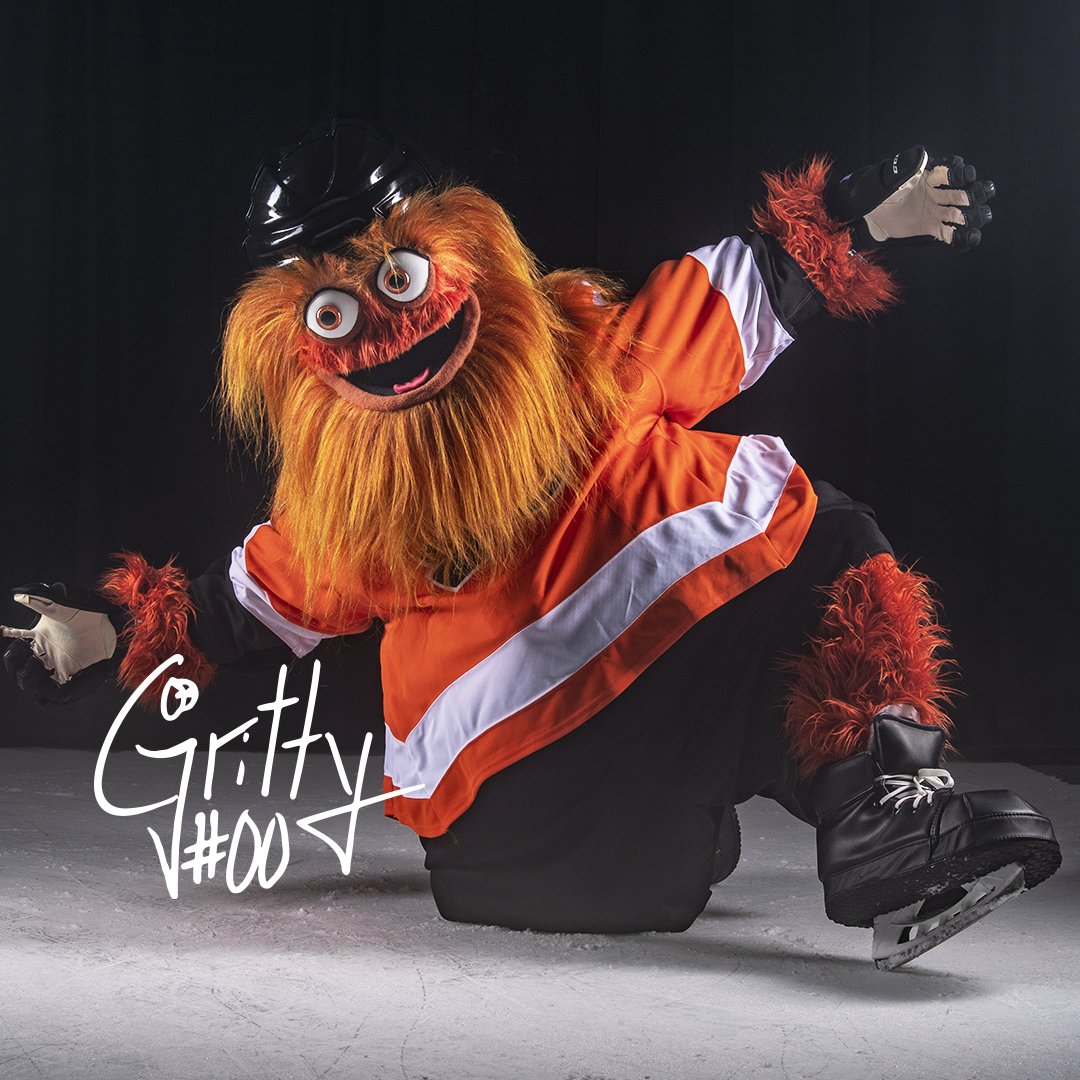

Like any once-and-hopefully-future resident of the great city of Philadelphia, I’m entranced by Gritty, the new mascot for the Philadelphia Flyers. Now, full disclosure: the Flyers were not one of the teams I initially adopted when I moved to Philadelphia, because my hometown Detroit Red Wings were still great in 2002, and so I was all set, hockey-wise. I picked up the New York Rangers when I moved to New York in 2012, when Henrik Lundqvist was winning Vezinas and stunting on fools. But Gritty is sufficiently compelling that I might have to add the Flyers to the Eagles, Phillies, and Sixers, becoming a full Philadelphia sports fan.
Why is Gritty captivating the world? Is it because or despite of his muppet-like googly eyes and shaggy appearance? I mean, when you really dig into it, it’s not like there’s a whole lot there. But a sufficiently advanced cipher can become a multilayered text to the devout, and that’s what’s happened with Gritty. Fans turned what was briefly an object of ridicule into an icon of devotion. And a legend was born.
For a deeper look into the Gritty phenomenon, seek no further than The Ringer, the website that was designed from its origins in the late, beloved Grantland to get to the bottom of sports questions like this. Michael Baumann’s “The Monster In The Mirror” is insightful, and nearly exhaustive, in answering why people inside and outside of Philadelphia have taken to Gritty so strongly. It also doubles as a psychological profile of one of my favorite cities and their sports fans.
Some excerpts:
In the past two and a half months, Gritty has proven to be an overwhelming success as a mascot. More than that, he’s become a legitimate cultural phenomenon, a weird and scary avatar for a weird and scary time. He is all things to all people.
“Gritty is fairly appalling, pretty insurrectionary for a mascot, and I don’t think there’s any question that that’s our kind of symbol,” says Helen Gym, an at-large member of the Philadelphia City Council. “There’s nothing more Philly than being unapologetically yourself.”
And:
The Flyers, Raymond says, had long resisted the idea of creating a mascot, at the insistence of founding owner Ed Snider, whom Raymond calls “old-school.” The Flyers unveiled a furry mascot called Slapshot in 1976 but quickly shelved it, leaving the team without a mascot for more than 40 years. But after Snider’s death in 2016, the team’s marketing department pushed ownership to reconsider, Raymond says, and after overcoming so much institutional inertia, they weren’t going to be half-hearted about their new mascot.
One part of doing a mascot right, Raymond says, is sticking to the bit no matter what, rather than submitting the mascot to the public for approval, a lesson learned from the Sixers’ failed mascot vote in 2011. Philadelphians, and people on the internet in general, can sense uncertainty and will punish it.
On Gritty’s Hensonian roots:
Mascots are always at least a little silly and ridiculous because at their core, they’re created more for children than adults. Gritty is no exception. His hands squeak, and his belly button—which Raymond calls a “woobie”—is a brightly colored outie. The woobie, says Raymond, was the brainchild of Chris Pegg, who plays Rockey the Redbird for the Triple-A Memphis Redbirds and is a mutual friend of Raymond and Flyers senior director of game presentation Anthony Gioia.
When the Flyers unveiled such a weird, menacing mascot, it brought to mind something Frank Oz said about his longtime collaborator and Muppets creator Jim Henson: “He thought it was fine to scare children. He didn’t think it was healthy for children to always feel safe.” According to Raymond, in any sufficiently large group of children, a mascot, even a familiar one, will make at least one of them cry. Not Gritty.
“I’d never seen a mascot rollout anywhere where I didn’t see at least one kid running, crying in terror, trying to grab on to their mother’s legs,” Raymond says of the Please Touch Museum rollout. “I didn’t see any of that [with Gritty]. The kids were dancing and hollering and calling for him to come over, but no kid looked terrified.”
And on Gritty’s additional incarnation as the subject and vehicle for leftist political memes:
Some Gritty memes, however, are not just funny or scary, but overtly political. Gym’s resolution addressed this issue head-on; “non-binary leftist icon” was one of the descriptions quoted in the resolution. The resolution itself goes on to praise Gritty for his status as a political symbol: “Gritty has been widely declared antifa, and was subject to attempted reclamation in the editorial pages of The Wall Street Journal. It has been argued that he ‘conveys the absurdity and struggle of modern life under capitalism’ and that he represents a source of joyful comic respite in a time of societal upheaval.”…
“The great thing about memes—as ridiculous as this sounds—is they create an instant mass internet mobilization,” FWG says. “Memes can be used to perpetuate systematic oppression, or they can be used to burn down the prison-industrial system or talk about police brutality.”
This identity is independent from — this is to say, it has been thoroughly stolen from — Gritty’s original role as a corporate sports mascot.
There’s a danger to wrapping up one’s identity in anything one can’t control, whether it’s an artist, a sports team, or a fuzzy orange monster. And if Gritty played it safe, he’d stop being worth investing in; the reason Gritty is so popular is because he’s weird and unpredictable in a way that isn’t cultivated to be “edgy.” Fear of being let down might just be the price of trying to live with empathy in a society that frequently elevates the cruel. It’s worth thinking about something FWG said: that their Gritty is not the same thing as the Flyers mascot.
“I think that the spirit of Gritty will be fulfilled through the proletariat,” FWG says. “As the spirit of Gritty moves people, that’s how the people will act.”
This is serious business! But as Walter Benjamin wrote, in a time of crisis, the here-and-now becomes shot through with messianic time. Gritty recalls the Phillie Phanatic, Sesame Street’s muppets, and Blastaar from the Fantastic Four, but puts all of their energy to use in a sense of futurity, that hope for the future that sports fandom echoes, however dimly. To quote Benjamin again:
It is well-known that the Jews were forbidden to look into the future. The Torah and the prayers instructed them, by contrast, in remembrance. This disenchanted those who fell prey to the future, who sought advice from the soothsayers. For that reason the future did not, however, turn into a homogenous and empty time for the Jews. For in it every second was the narrow gate, through which the Messiah could enter.
It’s ridiculous to see Gritty, the googly-eyed, outie-bellybuttoned Philadelphia Flyers mascot, as a messianic figure of the revolutionary left. But is that any more ridiculous than everything else that is happening in our fucked-up present? No. No, it is not.















Stay Connected