kottke.org posts about racism
With the help of Harvard historian Khalil Gibran Muhammad, this video from BuzzFeed documents investigations into police brutality and racism from the past century and how reforms based on those investigations have not brought about meaningful change. These reports — exploring the causes of unrest in Chicago in 1919, Harlem in 1935 & 1943, LA in 1965, Ferguson in 2014 — demonstrate again and again the discriminent violence committed against Black people by the police, and yet that violence and racism continues until the next investigation is conducted with the same conclusion.
In this special video edition of the Code Switch podcast, host Gene Demby explores the dangers of running while Black and why the safety of Black runners has not been given the same sort of attention as the safety of white women. The most striking bit of the video for me was right in the beginning when Demby debunks the myth of “all you need to run is a pair of shoes”.
When we runners talk about running — or let’s be real — when we evangelize about it, we talk a lot about how democratic it is. But it’s not really that simple. You’re gonna want gear, which costs money. Then there’s the issue of actual physical space. You want sidewalks that aren’t jagged, trails that aren’t overgrown, air that’s clean enough to breathe. (So ideally you don’t live near landfills or power plants or factories.) So yeah… all you need are shoes. And space. And money. And time. Oh and you also need something from the people around you — the sense that you belong in that space. Women don’t always get that luxury. And neither do runners of color.
Even a seemingly simple thing like running and who can do it is affected by decades of policy decisions that disproportionately favor residents of predominantly white neighborhoods.
You’ve probably seen the photograph: Tommie Smith and John Carlos each raising a black-gloved fist during the playing of the US nation anthem during the medals ceremony at the 1968 Summer Olympic Games in Mexico City. But as this video explains, their protest was a part of a larger effort to use the Olympics to highlight racial inequality in American sports and society.
After watching the video, you might be interested in reading about the aftermath of the protest. Smith and Carlos were both suspended from the US team and expelled from the Games. They were both subject to abuse from the American press and received death threats. Australian Peter Norman, who had come in second and supported the protest, was ostracized in his own country. But when Norman died in 2006, both Smith and Carlos were pallbearers at this funeral.
This video provides a quick overview of the history of policing in America through the lens of race, from the slave patrols in the South to the violent and discriminatory policing of Black migrants in the North in the midst the Great Migration. At its conclusion, historian Khalil Gibran Muhammad, author of The Condemnation of Blackness, asks a very direct question:
And so the question that has to be asked in the wake of George Floyd — and I think this question is being asked and answered by more white people than I’ve seen in my lifetime is — do white people in America still want the police to protect their interests over the rights and dignity and lives of Black and, in too many cases, brown, Indigenous, and Asian populations in this country?
This video is a snippet from an hour-long podcast episode of NPR’s Throughline called American Police (transcript here). (via @GeeDee215)
For What the police really believe, Vox’s Zack Beauchamp interviewed several former police officers and policing experts to find out how police think of themselves, their jobs, and the communities they are supposed to be protecting and serving.
Police officers across America have adopted a set of beliefs about their work and its role in our society. The tenets of police ideology are not codified or written down, but are nonetheless widely shared in departments around the country.
The ideology holds that the world is a profoundly dangerous place: Officers are conditioned to see themselves as constantly in danger and that the only way to guarantee survival is to dominate the citizens they’re supposed to protect. The police believe they’re alone in this fight; police ideology holds that officers are under siege by criminals and are not understood or respected by the broader citizenry. These beliefs, combined with widely held racial stereotypes, push officers toward violent and racist behavior during intense and stressful street interactions.
In a powerful video for the Movement For Black Lives, Daveed Diggs asks: “What, to My People, is the Fourth of July?”
What, to my people, is the Fourth of July? My people, who are failed every day by every country, sleepless in the long night, terrorized by fireworks, we who have cried salt baths for our kin.
Look at all we have borne for you: arms, armistice, the sweetest fruits, flesh of children hidden away from the ugly summer of their own blood — we are on the front lines. Help me, tell me, what do we tell the children of your Fourth of July? What is death to a daughter? What is river to a sea? Where is the country where my people are safe?
Ancestors set the table send dream mares in high supply. Too heavy, too spent, too hot to cook, no promise beyond the sparkly simple bombs. Keep your holiday, your hunger, the blood in your teeth. Police parade down streets, proud descendants of the slave patrol. Theater of denial, a propaganda pageant, and we are on the front lines all summer. My uncle can’t sleep and he was born free. And he ain’t never been.
The text performed by Diggs — written by Safia Elhillo, Danez Smith, Lauren Whitehead, W. Kamau Bell, Angel Nafis, Idris Goodwin, Pharoahe Monch, Camonghne Felix, and Nate Marshall — was inspired by Frederick Douglass’ July 5, 1852 speech, in which he asked, “What, to the American slave, is your Fourth of July?”
Fellow-citizens, pardon me, allow me to ask, why am I called upon to speak here to-day? What have I, or those I represent, to do with your national independence? Are the great principles of political freedom and of natural justice, embodied in that Declaration of Independence, extended to us? and am I, therefore, called upon to bring our humble offering to the national altar, and to confess the benefits and express devout gratitude for the blessings resulting from your independence to us?
In this long and interesting piece for the NY Times, The Warmth of Other Suns author Isabel Wilkerson explains America’s Enduring Caste System.
A caste system is an artificial construction, a fixed and embedded ranking of human value that sets the presumed supremacy of one group against the presumed inferiority of other groups on the basis of ancestry and often immutable traits, traits that would be neutral in the abstract but are ascribed life-and-death meaning in a hierarchy favoring the dominant caste, whose forebears designed it. A caste system uses rigid, often arbitrary boundaries to keep the ranks apart, distinct from one another and in their assigned places.
Throughout human history, three caste systems have stood out. The lingering, millenniums-long caste system of India. The tragically accelerated, chilling and officially vanquished caste system of Nazi Germany. And the shape-shifting, unspoken, race-based caste pyramid in the United States. Each version relied on stigmatizing those deemed inferior to justify the dehumanization necessary to keep the lowest-ranked people at the bottom and to rationalize the protocols of enforcement. A caste system endures because it is often justified as divine will, originating from sacred text or the presumed laws of nature, reinforced throughout the culture and passed down through the generations.
The article is an adapted excerpt from her forthcoming book, Caste: The Origins of Our Discontents:
Linking the caste systems of America, India, and Nazi Germany, Wilkerson explores eight pillars that underlie caste systems across civilizations, including divine will, bloodlines, stigma, and more. Using riveting stories about people — including Martin Luther King, Jr., baseball’s Satchel Paige, a single father and his toddler son, Wilkerson herself, and many others — she shows the ways that the insidious undertow of caste is experienced every day. She documents how the Nazis studied the racial systems in America to plan their out-cast of the Jews; she discusses why the cruel logic of caste requires that there be a bottom rung for those in the middle to measure themselves against; she writes about the surprising health costs of caste, in depression and life expectancy, and the effects of this hierarchy on our culture and politics. Finally, she points forward to ways America can move beyond the artificial and destructive separations of human divisions, toward hope in our common humanity.
The Warmth of Other Suns is one of my favorite books I’ve read in the past decade, so I’m very much looking forward to her new one.
From Aric Jenkins, a collection of articles on “how race continues to shape the design and infrastructure of American cities”. I’m interested to read Corinne Ramey’s piece on America’s Unfair Rules of the Road:
In the shadow of the bridge sits a small neighborhood called the West Side, where the asthma rate is more than four times the national average, and residents report a host of other health issues. Advocates say the thousands of trucks driving overhead spew harmful diesel emissions and other particulates into their community. The pollutants hover in the air, are absorbed into buildings and houses, and find their way into the lungs of neighborhood residents, who are primarily people of color. “It’s constant asthma problems on the West Side,” says Sharon Tell, a local resident.
And Un-Making Architecture from WAI Think Tank:
Buildings are never just buildings. Buildings respond to the political foundations of the institutions that fund, envision, and desire them. Buildings are physical manifestations of the ideologies they serve. Although a naively detached or romantic position may be able to render buildings as semi-autonomous artifacts capable of sheltering or enveloping space, this depoliticized attitude overlooks their historical and material relationship to regimes of violence and terror. Buildings can protect but they can also confine, instill fear, crush, oppress. Buildings can school, and foment hospitality but can imprison and torture. Buildings can be tools for ethnic segregation, cultural destruction and historical erasure. Buildings can reinforce the status quo and aide in the implementation of settler-colonial desires of expansionism. An anti-racist democratization of access is only possible through the decolonization of buildings and public spaces. Architects should be aware of the programs of the buildings they design and be held accountable for doing so.
In an opinion piece for the NY Times, Caroline Randall Williams writes You Want a Confederate Monument? My Body Is a Confederate Monument. I’ve never read an opening like this; I could barely continue:
I have rape-colored skin. My light-brown-blackness is a living testament to the rules, the practices, the causes of the Old South.
If there are those who want to remember the legacy of the Confederacy, if they want monuments, well, then, my body is a monument. My skin is a monument.
Only the truth is so devastating. Please read the entire essay. Williams will be reading this essay on Instagram on Tuesday, June 30 at 7pm ET — I’ll be there. And I just bought her book, Lucy Negro, Redux: The Bard, a Book, and a Ballet.
Update: Late last week, Williams answered some queries and comments from the readers of her piece.
For her series Counternarratives, artist and media critic Alexandra Bell takes newspaper articles and layouts from the NY Times that demonstrate racial bias and fixes them. For example, Bell took the notorious double profile of Michael Brown and his killer Darren Wilson and placed the focus entirely on Brown:

In this video, Bell explains her process:
I think everything is about race. Black communities, gay communities, immigrant communities feel a lot of media representations to be inadequate, biased. There’s a lot of reporting around police violence and black men, and I realized a lot of the arguments that we were having were about depictions. I started to wonder how different would it be if I swapped images or changed some of the text.
See also Kendra Pierre-Louis’ recent article for Nieman Lab: It’s time to change the way the media reports on protests. Here are some ideas.
In a piece for the NY Times called What Is Owed, Nikole Hannah-Jones argues that because of its sanction of slavery and subsequent legalized racial segregation and discrimination, it is time for the United States government to pay its debt to Black Americans in form of reparations.
To summarize, none of the actions we are told black people must take if they want to “lift themselves” out of poverty and gain financial stability — not marrying, not getting educated, not saving more, not owning a home — can mitigate 400 years of racialized plundering. Wealth begets wealth, and white Americans have had centuries of government assistance to accumulate wealth, while the government has for the vast history of this country worked against black Americans doing the same.
“The cause of the gap must be found in the structural characteristics of the American economy, heavily infused at every point with both an inheritance of racism and the ongoing authority of white supremacy,” the authors of the Duke study write. “There are no actions that black Americans can take unilaterally that will have much of an effect on reducing the wealth gap. For the gap to be closed, America must undergo a vast social transformation produced by the adoption of bold national policies.”
This piece is one of the best things I’ve read this year. It is clear, focused, powerful, and persuasive. There is no amount of money that anyone could ever pay to make up for the 400+ years of absolute shit rained down on Black people by the United States of America and its precursors, but nevertheless, reparations are the only just and moral way forward for the United States.
P.S. Here’s the Duke study mentioned in the excerpt above: What We Get Wrong About Closing the Racial Wealth Gap. And the book containing a detailed plan for reparations mentioned by Hannah-Jones is From Here to Equality: Reparations for Black Americans in the Twenty-First Century (ebook).
Update: Terry Gross interviewed Hannah-Jones on Fresh Air about reparations.
I think that reparations can’t just be any one thing. I think that you have to have targeted investment in Black communities and Black schools that have been generationally under-resourced. You certainly need to have a commitment to strong enforcement of existing civil rights laws, because reparations don’t do any good if you’re still facing rampant employment and housing and educational discrimination. But the center of any reparations program has to be cash payments. The only thing that closes a wealth gap is money.
Former NFL linebacker and sports media personality Emmanuel Acho has started a video series on YouTube called Uncomfortable Conversations with a Black Man. From the first episode (of two), here’s his mission statement:
In the midst of all this chaos in our world, so many of y’all have reached out to me. And by y’all, I mean white people have reached out to me asking, “How can I help? How can I join in? How can I stand with you?” So I’ve created this for you because in order to stand with us and people that look like me, you have to be educated on issues that pertain to me. And fully educated so that you can feel the full level of pain so that you can have full understanding. I fervently believe that if the white person is your problem only the white person can be your solution. And so this is made for you my white brothers and sisters to increase your level of understanding so that you can increase your level of compassion and lead ultimately to change.
For the second episode, Acho sat down with fellow Austin resident Matthew McConaughey and yes, the conversation is a little cringe-y at times:
After watching that, you might be interested in reading Langston Hughes’ poem Let America Be America Again.
O, let America be America again-
The land that never has been yet-
And yet must be-the land where every man is free.
The land that’s mine-the poor man’s, Indian’s, Negro’s, ME-
Who made America,
Whose sweat and blood, whose faith and pain,
Whose hand at the foundry, whose plow in the rain,
Must bring back our mighty dream again.
Netflix has put When They See Us, Ava DuVernay’s 4-episode mini-series about the Central Park Five, in front of their paywall for free viewing. Here’s the trailer:
The 2013 Ken Burns documentary The Central Park Five is available to watch on the PBS site and also on Amazon.
As previously noted, DuVernay’s 13th and Selma are also both available to watch online for free.
In his 2018 review of several books about Nazism and Adolf Hitler, Alex Ross notes that Hitler took inspiration for the Third Reich’s anti-Semitism and the Holocaust from the United States’ genocide against indigenous peoples, treatment of African Americans (both during and after slavery), and restrictive immigration policies.
The Nazis were not wrong to cite American precedents. Enslavement of African-Americans was written into the U.S. Constitution. Thomas Jefferson spoke of the need to “eliminate” or “extirpate” Native Americans. In 1856, an Oregonian settler wrote, “Extermination, however unchristianlike it may appear, seems to be the only resort left for the protection of life and property.” General Philip Sheridan spoke of “annihilation, obliteration, and complete destruction.” To be sure, others promoted more peaceful-albeit still repressive-policies. The historian Edward B. Westermann, in “Hitler’s Ostkrieg and the Indian Wars” (Oklahoma), concludes that, because federal policy never officially mandated the “physical annihilation of the Native populations on racial grounds or characteristics,” this was not a genocide on the order of the Shoah. The fact remains that between 1500 and 1900 the Native population of U.S. territories dropped from many millions to around two hundred thousand.
America’s knack for maintaining an air of robust innocence in the wake of mass death struck Hitler as an example to be emulated. He made frequent mention of the American West in the early months of the Soviet invasion. The Volga would be “our Mississippi,” he said. “Europe — and not America — will be the land of unlimited possibilities.” Poland, Belarus, and Ukraine would be populated by pioneer farmer-soldier families. Autobahns would cut through fields of grain. The present occupants of those lands — tens of millions of them — would be starved to death. At the same time, and with no sense of contradiction, the Nazis partook of a long-standing German romanticization of Native Americans. One of Goebbels’s less propitious schemes was to confer honorary Aryan status on Native American tribes, in the hope that they would rise up against their oppressors.
Jim Crow laws in the American South served as a precedent in a stricter legal sense. Scholars have long been aware that Hitler’s regime expressed admiration for American race law, but they have tended to see this as a public-relations strategy — an “everybody does it” justification for Nazi policies. Whitman, however, points out that if these comparisons had been intended solely for a foreign audience they would not have been buried in hefty tomes in Fraktur type. “Race Law in the United States,” a 1936 study by the German lawyer Heinrich Krieger, attempts to sort out inconsistencies in the legal status of nonwhite Americans. Krieger concludes that the entire apparatus is hopelessly opaque, concealing racist aims behind contorted justifications. Why not simply say what one means? This was a major difference between American and German racism.
The Atlantic was founded in 1857 and in its early days was an outlet for prominent voices speaking out against slavery. Editor Gillian White has compiled a list of the magazine’s writing on race and racism in America from deep in the archive to the present day. It includes writing from Julia Ward Howe, Frederick Douglass, W.E.B. Du Bois, Booker T. Washington, Martin Luther King Jr., and Stokely Carmichael along with pieces from modern voices like Bree Newsome, Eve Ewing, Ta-Nehisi Coates, Ibram X. Kendi, and Nikole Hannah-Jones. In introducing the collection, White writes:
Understanding the present moment requires grappling with a history stained by racial inequity, violence, and the constant fight for forward progress. In a century and a half of writing stories about race in America, The Atlantic has published works that have improved the broad understanding of injustice in America, and also works that furthered ideas and theories that ultimately were proved wrong or harmful. To comprehend the current state of the country, we must consider the aftereffects of both categories. We must also take into account the fact that these stories, in aggregate, are overwhelmingly written by men.
And here are a few pieces I picked out for my own personal reading list:
Reconstruction by Frederick Douglass, December 1866. “No republic is safe that tolerates a privileged class, or denies to any of its citizens equal rights and equal means to maintain them.”
The Awakening of the Negro by Booker T. Washington, September 1896. “I wish my readers could have the chance that I have had of going into this community. I wish they could look into the faces of the people and see them beaming with hope and delight.”
The Negro Is Your Brother (Letter From Birmingham Jail) by Martin Luther King Jr., August 1963. “Whatever affects one directly, affects all indirectly. Never again can we afford to live with the narrow, provincial ‘outside agitator’ idea. Anyone who lives inside the United States can never be considered an outsider anywhere within its bounds.”
The Prison-Industrial Complex by Eric Schlosser, December 1998. “The United States now imprisons more people than any other country in the world — perhaps half a million more than Communist China. The American inmate population has grown so large that it is difficult to comprehend: imagine the combined populations of Atlanta, St. Louis, Pittsburgh, Des Moines, and Miami behind bars.”
The Case for Reparations by Ta-Nehisi Coates, June 2014. “And so we must imagine a new country. Reparations — by which I mean the full acceptance of our collective biography and its consequences — is the price we must pay to see ourselves squarely.”
In yesterday’s post about police abolition, I linked to a two-part podcast conversation between Chenjerai Kumanyika and Ruth Wilson Gilmore. I listened to the first part yesterday afternoon after posting and it was excellent, full of serious knowledge and deep context about a massive and complex American problem. But I wanted to focus here on something from the closing moments of the episode that I had never heard before: Gilmore’s definition of racism. Acknowledging that it’s a “mouthful”, she defined racism in her book Golden Gulag as “the state-sanctioned and/or extra-legal production and exploitation of group-differentiated vulnerability to premature death”.
I do not have the expertise or desire to wade into the often-contentious debate about what racism is or is not (see here for instance), but what I like about Gilmore’s take is how it explicitly includes the consequence of racism as an integral part of the definition. Racism is death — there’s a sense of moral urgency when you describe it like that, a clarity that’s absent if you’re just talking about a belief in the superiority of one race over another or even the systemic application or sanction of such prejudice.
The Atlantic is releasing their first feature-length documentary later this month.1 The film is called White Noise and it’s about the white nationalist movement in the US. Director Daniel Lombroso spent four years embedded in the “alt-right” movement to figure out how it works.
Progressives like to believe that racism is an opiate of the ignorant. But the alt-right’s leaders are educated and wealthy, groomed at some of America’s most prestigious institutions. The more time I spent documenting the movement, the more ubiquitous I realized it was. I bumped into one subject dancing in Bushwick with his Asian girlfriend, and another walking around DuPont Circle hitting a vape. Their racism is woven into the fabric of New York, Washington, D.C., and Paris, just as much as Birmingham, Alabama, or Little Rock, Arkansas.
During a visit to Richard Spencer’s apartment in Alexandria, Virginia, I began to understand how the alt-right works. Evan McLaren, a lawyer, wrote master plans on a whiteboard. A band of college kids poured whiskey for Spencer, adjusted his gold-framed Napoleon painting, and discussed the coming “Identitarian” revolution. Spencer offered a sense of historical purpose to his bored, middle-class followers. In his telling, they weren’t just “white Americans,” but descendants of the Greeks and Romans. “Myths are more powerful than rationality,” Spencer told me. “We make life worth living.”
White Noise is about the seductive power of extremism. Hatred feels good. But the fix is fleeting. As the film progresses, the subjects reveal the contradictions at the heart of their world. Southern advocates for traditional gender roles, but resents the misogyny and sexism of her peers. Cernovich warns that “diversity is code for white genocide,” but has an Iranian wife and biracial kids. Spencer swears he’ll lead the white-nationalist revolution — until it’s more comfortable for him to move home to live with his wealthy mother in Montana. For so many who feel lost or alone, these avatars of hate offer a promise: Follow us, and life will be better.
I mean, I’d roll my eyes if these assholes weren’t so effective and dangerous.
The film is premiering online at AFI on June 20. There doesn’t seem to be a trailer or any clips available (which seems odd) but I’ll update this post if one materializes.
In The Atlantic, epidemiologists Julia Marcus and Gregg Gonsalves explain why public health officials are not being hypocritical in their support of the antiracism protests around the country.
At its core, the argument being leveled against public-health experts is that the reason for the protests shouldn’t matter. The coronavirus doesn’t care whether it’s attending an anti-lockdown protest or an anti-racism one. But these two kinds of protests are not equivalent from a public-health perspective. Some critics might argue that the anti-lockdown protests promoted economic activity, which can help stave off the health implications of poverty. (On this count, public-health experts were ahead of the curve: Many — including one of us — were advocating for a massive infusion of assistance to individual Americans as early as March.) But these protests were organized by pro-gun groups that believe the National Rifle Association is too compromising on gun safety. Egged on by the president to “save your great 2nd Amendment,” anti-lockdown protesters stormed government buildings with assault rifles and signs reading COVID-19 IS A LIE. The anti-lockdown demonstrations were explicitly at odds with public health, and experts had a duty to oppose them. The current protests, in contrast, are a grassroots uprising against systemic racism, a pervasive and long-standing public-health crisis that leads to more than 80,000 excess deaths among black Americans every year.
If “conservative commentators” cared at all about keeping people safe from Covid-19 infection, they would have denounced the I-Need-A-Haircut protests as reckless and they didn’t. Instead, they engage in these bad faith arguments that are just designed to stir up outrage.
Gonsalves wrote a thread on Twitter a few days ago that’s relevant here as well.
The risk to all of us was inflamed by an absolute decision at the highest levels that this epidemic was not worth an all-out, coordinated, comprehensive national mobilization. It took weeks for the President to even agree that the epidemic wouldn’t go away on its own.
The US, the richest nation in the world, then couldn’t get it together to scale-up the number of tests we needed to understand what was going on in our communities with SARS-COV-2, and in the end said it was up to the states to figure it all out.
And then this is the last word as far as I’m concerned:
We’ve all been put at far more jeopardy during this pandemic by our political leaders than by the people on the streets over the past week or so.

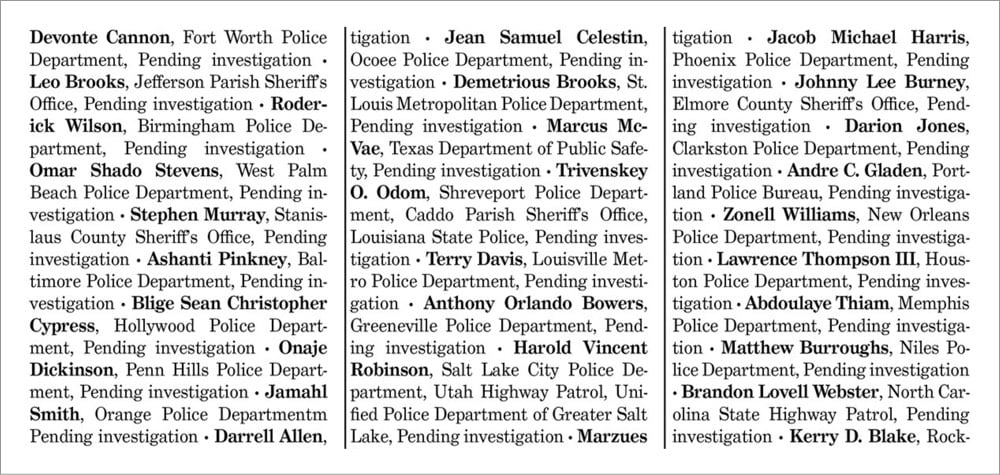
On Sunday May 24, the NY Times gave over their entire front page to listing the names of hundreds of victims of Covid-19 in the US. It was an iconic gesture that focused people’s attention on both the overall death toll and the stories & lives of the individual people who had been killed by the disease.
The Incalculable Loss Project has repurposed this design to honor some of the 7,000 Black Americans killed by police since 2000 and to ask why media outlets like the Times haven’t given “the same attention to this epidemic as they did Covid-19”. Each person’s name is accompanied by the name of the officer’s police department and the current status of the investigation into the killing (overwhelmingly “pending investigation”).
In this video for NPR, Gene Demby summarizes the history of housing segregation in America and how it’s a factor for current differences in health (poorer), wealth (much less), education (underfunded), and policing (much more aggressive) for Black communities in US cities.
If you look at the way housing segregation works in America, you can see how things ended up this way. Once you see it, you won’t be able to unsee it.
When you’re talking about housing policy in America, Kimberly Jones’ Monopoly analogy starts to sound a lot less metaphorical and more literal: if Black people cannot buy houses or can only buy houses on certain streets, they will not be able to build wealth like others can.
For more on housing segregation, check out historian Richard Rothstein’s The Color of Law: A Forgotten History of How Our Government Segregated America. From a 2017 interview with Rothstein:
The federal government pursued two important policies in the mid-20th century that segregated metropolitan areas. One was the first civilian public housing program which frequently demolished integrated neighborhoods in order to create segregated public housing.
The second program that the federal government pursued was to subsidize the development of suburbs on a condition that they be only sold to white families and that the homes in those suburbs had deeds that prohibited resale to African-Americans. These two policies worked together to segregate metropolitan areas in ways that they otherwise would never have been segregated.
Rothstein talked about the book with Ta-Nehisi Coates during a conversation at Politics and Prose Bookstore.
Update: This is excellent: you can explore the maps created by the federal government’s Home Owners’ Loan Corporation at Mapping Inequality by the University of Richmond’s Digital Scholarship Lab.
These grades were a tool for redlining: making it difficult or impossible for people in certain areas to access mortgage financing and thus become homeowners. Redlining directed both public and private capital to native-born white families and away from African American and immigrant families. As homeownership was arguably the most significant means of intergenerational wealth building in the United States in the twentieth century, these redlining practices from eight decades ago had long-term effects in creating wealth inequalities that we still see today.
(via @masonadams)
Do me a favor and take about 7 minutes to watch author Kimberly Jones’ off-the-cuff “rant” (her words) about how rioting and looting fit within the larger narrative of the economic oppression of Black people in America. I’ve never heard the long, shameful, and deadly history of white supremacy in America summed up any better or more succinctly than Jones does here. The Monopoly analogy in particular is fantastic.
When they say “Why do you burn down the community? Why do you burn down your own neighborhood?” It’s not ours! We don’t own anything! We don’t own anything! Trevor Noah said it so beautifully last night: There’s a social contract that we all have — that if you steal or if I steal, then the person who is the authority comes in and they fix the situation. But the person who fixes the situation is killing us! So the social contract is broken. And if the social contract is broken, why the fuck do I give a shit about burning the fucking Football Hall of Fame, about burning the fucking Target? You broke the contract when you killed us in the streets and didn’t give a fuck! You broke the contract when for 400 years we played your game and built your wealth!
Update: Jones has signed a deal with Henry Holt and Company to write two books, one of which will be called “How We Can Win” and will be based on the video above.
Update: How We Can Win will be out in November and is now available for preorder.
Calling it one of their most requested videos, PBS’s Frontline has uploaded to YouTube their 1985 program on schoolteacher Jane Elliott’s powerful lesson in discrimination. The video shows how, in the wake of Martin Luther King Jr.’s assassination, Elliott divided her third-grade class into those with blue eyes and those with non-blue eyes and then instructed the non-blue-eyed group to treat the blue-eyed group as inferior. The resulting behavior is fascinating, upsetting, and illuminating.
Elliott went on to become a noted antiracism activist and has done blue eyes/brown eyes workshops with groups of adults and teens. And she goes hard at them — see this video and this video for instance.
I’m trying to get the people who participate in this exercise the opportunity to find out how it feels like to be something other than white in this society. ‘Alright people, I’m Jane Elliott and I’m your resident bitch for the day and make no mistake about that, that is exactly what this is about.’ I do this in a mean, nasty way because racism, sexism, ageism, homophobia, ethnocentrism are mean and nasty.
I would also highly recommend watching this brief clip of a talk by Elliott. In less than a minute, she deftly skewers the idea that racial discrimination doesn’t exist in America and calls out White Americans’ complicity in allowing it to persist.
I want every white person in this room who would be happy to be treated as this society in general treats our black citizens — if you as a white person would be happy to receive the same treatment that our black citizens do in this society, please stand.
[Nobody stands.]
You didn’t understand the directions. If you white folks want to be treated the way blacks are in this society, stand. Nobody’s standing here. That says very plainly that you know what’s happening, you know you don’t want it for you. I want to know why you’re so willing to accept it or to allow it to happen for others.
Freedom for some is not freedom.
Update: Alisha Haridasani Gupta recently interviewed Elliott for the NY Times. In it, she reveals that she doesn’t do her workshops anymore because people are increasingly close-minded.
I’ve been doing the exercise with adults for about 35 years. But in the last few years, I’ve only been doing speeches about it because we now live in a situation where people turn off immediately if they think they’re going to learn something counter to their beliefs, and I don’t want to be threatened with death anymore. I’m tired of receiving death threats.
In a powerful essay for The Atlantic, Ibram X. Kendi writes about The American Nightmare.
To be black and conscious of anti-black racism is to stare into the mirror of your own extinction. Ask the souls of the 10,000 black victims of COVID-19 who might still be living if they had been white. Ask the souls of those who were told the pandemic was the “great equalizer.” Ask the souls of those forced to choose between their low-wage jobs and their treasured life. Ask the souls of those blamed for their own death. Ask the souls of those who disproportionately lost their jobs and then their life as others disproportionately raged about losing their freedom to infect us all. Ask the souls of those ignored by the governors reopening their states.
The American nightmare has everything and nothing to do with the pandemic. Ask the souls of Breonna Taylor, Ahmaud Arbery, and George Floyd. Step into their souls.
Hi. I wanted to take today to compile a sampling of what Black people (along with a few immigrant and other PoC voices) are saying about the recent murders by police of Breonna Taylor and George Floyd, the murder of Ahmaud Arbery, the threatening of Christian Cooper with police violence by a White woman, the protests in Minneapolis & other places, and the unequal impact of the pandemic on communities of color, as well as what Black voices have said in the past about similar incidents & situations. This is not an exhaustive list of reaction & commentary — it’s just a sample. I’m not going to add anything to these voices, but I will share a few resources at the end of the post.
Please put your urge to judge on the shelf for a minute and just listen to your fellow human beings in all of their raw, righteous, and furious anger. I am trying to listen. Is America finally ready to listen? Are you ready?
Keeanga-Yamahtta Taylor, Of Course There Are Protests. The State Is Failing Black People.
This simultaneous collapse of politics and governance has forced people to take to the streets — to the detriment of their health and the health of others — to demand the most basic necessities of life, including the right to be free of police harassment or murder.
What are the alternatives to protest when the state cannot perform its basic tasks and when lawless police officers rarely get even a slap on the wrist for crimes that would result in years of prison for regular citizens? If you cannot attain justice by engaging the system, then you must seek other means of changing it. That’s not a wish; it’s a premonition.
Keeanga-Yamahtta Taylor again reacting to “American billionaires got $434 billion richer during the pandemic”:
This looting by billionaires is what sets fires and burns down stores. You do not get one without the other.
Jillian Sloane:
I wish America loved black people the way they love black culture.
Martin Luther King, Jr., The Other America (via Paul Octavious):
I think America must see that riots do not develop out of thin air. Certain conditions continue to exist in our society which must be condemned as vigorously as we condemn riots. But in the final analysis, a riot is the language of the unheard. And what is it that America has failed to hear? It has failed to hear that the plight of the Negro poor has worsened over the last few years. It has failed to hear that the promises of freedom and justice have not been met. And it has failed to hear that large segments of white society are more concerned about tranquility and the status quo than about justice, equality, and humanity. And so in a real sense our nation’s summers of riots are caused by our nation’s winters of delay. And as long as America postpones justice, we stand in the position of having these recurrences of violence and riots over and over again. Social justice and progress are the absolute guarantors of riot prevention.
Bakari Sellers (click through to watch the video):
It’s just so much pain. You get so tired. We have black children. I have a 15-year-old daughter. What do I tell her? I’m raising a son. I have no idea what to tell him. It’s just, it’s hard being black in this country when your life is not valued.
Black parents talk to their children about how to deal with the police:
Ruhel Islam, a Bangladeshi immigrant and owner of Gandhi Mahal Restaurant, which burned in Minneapolis:
Let my building burn, Justice needs to be served, put those officers in jail.
DiDi Delgado:
In the time between Eric Garner’s “I can’t breathe” and George Floyd’s “I can’t breathe” police in the United States killed at least (AT LEAST) 5,947 people. #WeCantBreathe
Ella Baker:
Until the killing of black men, black mothers’ sons, becomes as important to the rest of the country as the killing of a white mother’s son, we who believe in freedom cannot rest.
Peter Daou:
America, where it’s okay to kneel on a black man’s neck and murder him, but it’s “unpatriotic” to kneel in protest of that murder.
#BlackLivesMatter #TakeAKnee
Luvvie Ajay, About the Weary Weaponizing of White Women Tears:
White people will never have to deal with the fact that their skin is considered a weapon but they use their skins as ammunition by using all the privileges that come with it to terrorize the world. White women use their tears as pity me bombs all the time and it often instigates Black people being punished.
Ajay again:
I’ve traveled all over the world. And have never felt as unsafe as I do at home, in the United States.
Never.
@jxparisxo:
Can we stop calling it “police brutality” it’s murder, M-U-R-D-E-R
Nikole Hannah-Jones, Yes, Black America Fears the Police. Here’s Why.:
For those of you reading this who may not be black, or perhaps Latino, this is my chance to tell you that a substantial portion of your fellow citizens in the United States of America have little expectation of being treated fairly by the law or receiving justice. It’s possible this will come as a surprise to you. But to a very real extent, you have grown up in a different country than I have.
As Khalil Gibran Muhammad, author of The Condemnation of Blackness, puts it, “White people, by and large, do not know what it is like to be occupied by a police force. They don’t understand it because it is not the type of policing they experience. Because they are treated like individuals, they believe that if ‘I am not breaking the law, I will never be abused.’”
We are not criminals because we are black. Nor are we somehow the only people in America who don’t want to live in safe neighborhoods. Yet many of us cannot fundamentally trust the people who are charged with keeping us and our communities safe.
Jemele Hill:
Trump to the white people with AR-15s throwing a temper tantrum over a haircut — “Liberate”
Trump to those protesting the lack of justice in Minneapolis — “THUGS”
A whole, racist clown.
Tarana Burke:
A few years ago me and dude are out and come back to his car to find it vandalized. He parked by a driveway and partially blocked it and we concluded that the owners had vandalized the car. I get pissed and go knock on the door. They don’t answer so I’m yelling!
He’s telling me to calm down and forget it but I’m pissed! A few minutes later cop car rolls by and they stop and get out. I start to tell them what happened and they walk up on him and immediately start questioning him. I interrupt and say “excuse me HIS car was vandalized!”
The cops tell me to ‘be quiet’ and just as I’m about to turn all the way up on them he turns to me and says “Baby, please…” firmly. Then he calmly answers the cops questions even though they are rude and invasive. They take his license and keep asking ridiculous questions…
“What are you all doing here?”
“Did you get into an altercation earlier tonight?”
“If I knock on these people’s door what are they going to say?”
I was fuming. Now I’m nervous.
Damon Young, Thoughts on Forgiving Amy Cooper (aka ‘Darth Karen’), Who Got Fired, Banned From Central Park, and Lost Her Dog:
LOLOLOLOLOLOLOLOLOLOL…
Ibram X. Kendi (via Nicole Parker):
The greatest white privilege is life itself. People of color are being deprived of life.
Dr. Kendi again:
They say they can’t be racist because they are northerners. They say they can’t be racist because they are progressives. They say they can’t be racist because they are Democrats.
Why are they saying they can’t be racist? Because they are racist.
Dr. Kendi for a third time (he wrote a whole book about moments like these):
It feels like Black people were running for their lives from racist terror only to run into the murderous face of COVID-19, only to start running for their lives from COVID-19 only to run into the murderous face of racist terror.
Maurice Moe Mitchell:
If you have trouble imagining the concept of “police abolition,” look no further than the many live experiments being played out in upper middle class white suburbs across the country where people carry on their lives with little to no interaction with law enforcement.
Ernest Owens, I Have Not Missed the Amy Coopers of the World:
I’m doing better these days because staying home alone and practicing social distancing has meant I’m avoiding many of the racist encounters that used to plague my daily life.
The video that circulated this weekend of a white woman calling the police with a false report about threats by a black man who simply asked her to leash her dog in Central Park illustrates exactly why I’m so happy to be spending more time inside.
Blair Imani:
Murder is worse than property destruction. Every single time. Don’t let capitalism fool you.
Ruby Hamad, A White Damsel Leveraged Racial Power and Failed:
The damsel-in-distress archetype probably conjures up images of delicate maidens and chivalrous gentlemen. That is precisely what it is designed to do — for white people. To people of color, and especially African-Americans who have borne the brunt of her power in the United States, the image is very different. The damsel in distress is an illusion of innocence that deflects and denies the racial crimes of white society.
J. Drew Lanham, Birding While Black:
Up until now the going has been fun and easy, more leisurely than almost any “work” anyone could imagine. But here I am, on stop number thirty-two of the Laurel Falls Breeding Bird Survey (BBS) route: a large black man in one of the whitest places in the state, sitting on the side of the road with binoculars pointed toward a house with the Confederate flag proudly displayed. Rumbling trucks passing by, a honking horn or two, and curious double takes are infrequent but still distract me from the task at hand. Maybe there’s some special posthumous award given for dying in the line of duty on a BBS route-perhaps a roadside plaque honoring my bird-censusing skills.
Tyler Merritt, Before You Call the Cops:
Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez:
I’ll just say it: a lot of politicians are scared of the political power of the police, and that’s why changes to hold them accountable for flagrant killings don’t happen. That in itself is a scary problem.
We shouldn’t be intimidated out of holding people accountable for murder.
Ernest Owens:
BEFORE Y’ALL KEEP GOING: Christian Cooper could have had tattoos on his face, hated birds, been smoking a blunt and listening to Future, and #CentralParkAmy WOULD HAVE STILL BEEN AS GUILTY AND RACIST AND WRONG AF FOR TERRORIZING HIM.
Enough with the respectability politics.
Alicia Crosby:
I really can’t shake how profoundly evil it is to tear gas folks protesting the suffocation of a man by the police during a pandemic driven by a respiratory disease.
Shenequa Golding, Maintaining Professionalism In The Age of Black Death Is….A Lot:
Your black employees are exhausted.
Your black employees are scared.
Your black employees are crying in between meetings.
Your black employees have mentally checked out.
Your black employees are putting on a performance.
Charles Blow, How White Women Use Themselves as Instruments of Terror:
At a time of so much death and suffering in this country and around the world from the Covid-19 pandemic, it can be easy, I suppose, to take any incidents that don’t result in death as minor occurrences.
But they aren’t. The continued public assault on black people, particularly black men, by the white public and by the police predates the pandemic and will outlast it. This racial street theater against black people is an endemic, primal feature of the Republic.
Specifically, I am enraged by white women weaponizing racial anxiety, using their white femininity to activate systems of white terror against black men. This has long been a power white women realized they had and that they exerted.
Michael Harriot (from this thread):
There has NEVER been a successful protest movement in modern history that succeeded without violence.
Not Christianity. Not democracy. Not civil rights.
The choice is, which side is going to do the donate their blood?
We’re damn near out of blood to give.
So, if you want to change the system, history has repeatedly told us how to do it.
Burn.
That.
Shit.
Down.
And amen, motherfuckers.
James Baldwin (see also How to Cool It and, like, everything else Baldwin has ever written or said):
The reason that black people are in the streets has to do with the lives they’re forced to lead in this country. And they’re forced to lead these lives by the indifference and the apathy and a certain kind of ignorance — a very willful ignorance — on the part of their co-citizens.
Several people on social media have pointed to this list of 75 Things White People Can Do for Racial Justice, including several organizations you can donate to. Ibram X. Kendi compiled an antiracist reading list. I am not any sort of expert, but I personally have found much understanding in listening to the Seeing White podcast, reading Isabel Wilkerson’s The Warmth of Other Suns, and watching Eyes on the Prize, I Am Not Your Negro, & OJ: Made in America among other things. Thanks to everyone listed here for sharing their words and works with us.
There are a lot of different lenses you can use to look at how the United States and its government have confronted the Covid-19 pandemic. Race is a particularly useful one. As a reminder, here’s America’s current operating racial contract (from an Atlantic piece by Adam Serwer):
The implied terms of the racial contract are visible everywhere for those willing to see them. A 12-year-old with a toy gun is a dangerous threat who must be met with lethal force; armed militias drawing beads on federal agents are heroes of liberty. Struggling white farmers in Iowa taking billions in federal assistance are hardworking Americans down on their luck; struggling single parents in cities using food stamps are welfare queens. Black Americans struggling in the cocaine epidemic are a “bio-underclass” created by a pathological culture; white Americans struggling with opioid addiction are a national tragedy. Poor European immigrants who flocked to an America with virtually no immigration restrictions came “the right way”; poor Central American immigrants evading a baroque and unforgiving system are gang members and terrorists.
Serwer goes on to argue that the recently shifting American response to the pandemic, primarily in conservative circles, is due to an increasing awareness of which groups are bearing the brunt of the crisis: black and Latino Americans.
That more and more Americans were dying was less important than who was dying.
The disease is now “infecting people who cannot afford to miss work or telecommute-grocery store employees, delivery drivers and construction workers,” The Washington Post reported. Air travel has largely shut down, and many of the new clusters are in nursing homes, jails and prisons, and factories tied to essential industries. Containing the outbreak was no longer a question of social responsibility, but of personal responsibility. From the White House podium, Surgeon General Jerome Adams told “communities of color” that “we need you to step up and help stop the spread.”
This is a response that America is quite comfortable with because it fits with our racial contract, under which Jim Crow never actually ended. The US isn’t the only place this is happening btw. Early on, Singapore was praised for its response to the pandemic, but their reliance on and mistreatment of an underclass of migrant workers caused a secondary surge in cases.
Singapore is a small city-state with a population of just under 6 million inhabitants. On a per capita basis, it’s the second-richest country in Asia.
But its economy relies heavily on young men from Bangladesh, India and other countries who work jobs in construction and manufacturing. Singapore has no minimum wage for foreign or domestic employees. The foreign workers’ salaries can be as low as US$250 per month, but a typical salary is $500 to $600 a month.
British rapper and actor Riz Ahmed released an album last week called The Long Goodbye. It’s a breakup album with a twist — Ahmed is not breaking up with a partner but with a racist, post-Brexit Britain. A Guardian review describes it as “a conceptual work based around the idea that British Asians are locked in an abusive relationship with the UK and that the rising tide of racism spawned by Brexit might represent the moment at which they’ve finally been dumped”.
To accompany the album, Ahmed collaborated with director Aneil Karia to make a short film (embedded above). It starts out with a typical British domestic scene but after a few minutes, it becomes something else entirely. Be warned: this film is quite intense & dystopian. (via dunstan)
In the 1850s, the well-heeled residents of Manhattan were convinced the city needed a grand park like the European capitals had. And so, a park located in the middle of the city was proposed, a Central Park, if you will. The only problem? There were people living in the park’s proposed location, including Seneca village, a small, integrated, predominately black neighborhood.
It’s a story that goes back to the 1820s, when that part of New York was largely open countryside. Soon it became home to about 1,600 people. Among them was a predominantly black community that bought up affordable plots to build homes, churches and a school. It became known as Seneca Village. And when Irish and German immigrants moved in, it became a rare example at the time of an integrated neighborhood.
See also ‘The City Needed Them Out’.
I was travelling yesterday and so missed observing Martin Luther King Jr. Day on the site, but I ran across this quote from him on Instagram and wanted to highlight it. It’s from a radio speech King gave called To Minister to the Valley and like many of King’s speeches and writing, it concerns economic justice & equality.
Whenever the government provides opportunities in privileges for white people and rich people they call it “subsidized” when they do it for Negro and poor people they call it “welfare.” The fact that is the everybody in this country lives on welfare. Suburbia was built with federally subsidized credit. And highways that take our white brothers out to the suburbs were built with federally subsidized money to the tune of 90 percent. Everybody is on welfare in this country. The problem is that we all to often have socialism for the rich and rugged free enterprise capitalism for the poor. That’s the problem.
The quote and its sentiment reminds me of the White Affirmative Action episode (transcript) of the excellent Seeing White podcast series, in which Deena Hayes-Greene of the Racial Equity Institute asserts affirmative action in America has overwhelmingly favored and benefitted white people.
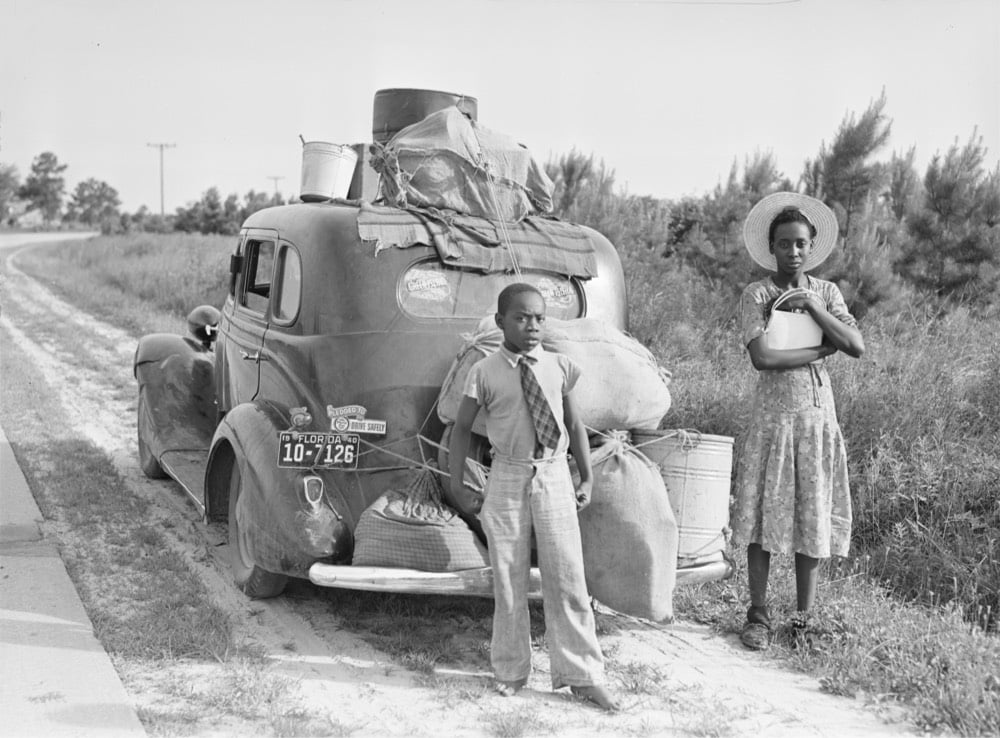
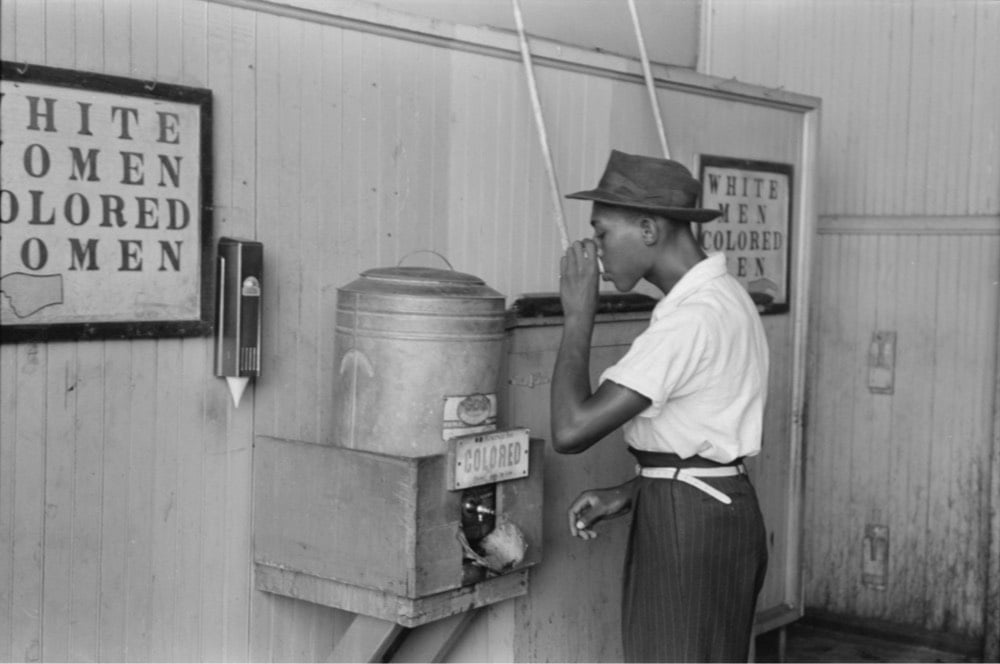
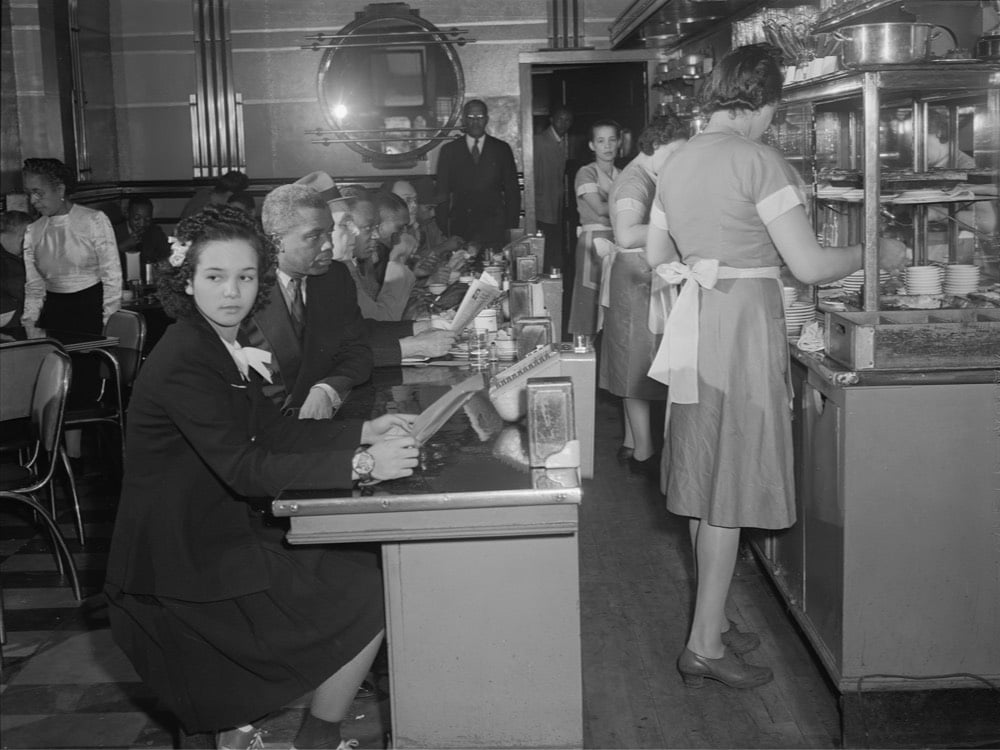



Librarians at the Library of Congress have created a new guide to finding photos of the Great Migration1 contained in their extensive collection. Here’s a blog post announcing the guide.
The “Searching for Images” page of the guide suggests search strategies for finding images related to the Great Migration. For example, when searching our online catalogs, researchers will be most successful when using keyword terms and subject headings that refer to specific places, people or events. I knew that “Black Belt” was sometimes used to describe the area on Chicago’s South Side that experienced a population boom during the Great Migration. Entering the keywords “black belt chicago” in the online catalog yielded a number of images of the area from April of 1941 from the Farm Security Administration / Office of War Information Collection.
I was just talking about the Great Migration with a friend last night. Neither of us had learned about it in school (not even college), even though it completely reshaped America in the 20th century. If you’re in a similar boat, I recommend starting with Isabel Wilkerson’s Pulitzer Prize-winning The Warmth of Other Suns. It’s impossible to understand contemporary American society without knowing the history of the Great Migration and Wilkerson’s book helped open my eyes to that. (via @john_overholt)
In a keynote address to the Anti-Defamation League, entertainer Sacha Baron Cohen calls the platforms created by Facebook, Google, Twitter, and other companies “the greatest propaganda machine in history” and blasts them for allowing hate, bigotry, and anti-Semitism to flourish on these services.
Think about it. Facebook, YouTube and Google, Twitter and others — they reach billions of people. The algorithms these platforms depend on deliberately amplify the type of content that keeps users engaged — stories that appeal to our baser instincts and that trigger outrage and fear. It’s why YouTube recommended videos by the conspiracist Alex Jones billions of times. It’s why fake news outperforms real news, because studies show that lies spread faster than truth. And it’s no surprise that the greatest propaganda machine in history has spread the oldest conspiracy theory in history- — the lie that Jews are somehow dangerous. As one headline put it, “Just Think What Goebbels Could Have Done with Facebook.”
On the internet, everything can appear equally legitimate. Breitbart resembles the BBC. The fictitious Protocols of the Elders of Zion look as valid as an ADL report. And the rantings of a lunatic seem as credible as the findings of a Nobel Prize winner. We have lost, it seems, a shared sense of the basic facts upon which democracy depends.
When I, as the wanna-be-gansta Ali G, asked the astronaut Buzz Aldrin “what woz it like to walk on de sun?” the joke worked, because we, the audience, shared the same facts. If you believe the moon landing was a hoax, the joke was not funny.
When Borat got that bar in Arizona to agree that “Jews control everybody’s money and never give it back,” the joke worked because the audience shared the fact that the depiction of Jews as miserly is a conspiracy theory originating in the Middle Ages.
But when, thanks to social media, conspiracies take hold, it’s easier for hate groups to recruit, easier for foreign intelligence agencies to interfere in our elections, and easier for a country like Myanmar to commit genocide against the Rohingya.
In particular, he singles out Mark Zuckerberg and a speech he gave last month.
First, Zuckerberg tried to portray this whole issue as “choices…around free expression.” That is ludicrous. This is not about limiting anyone’s free speech. This is about giving people, including some of the most reprehensible people on earth, the biggest platform in history to reach a third of the planet. Freedom of speech is not freedom of reach. Sadly, there will always be racists, misogynists, anti-Semites and child abusers. But I think we could all agree that we should not be giving bigots and pedophiles a free platform to amplify their views and target their victims.
Second, Zuckerberg claimed that new limits on what’s posted on social media would be to “pull back on free expression.” This is utter nonsense. The First Amendment says that “Congress shall make no law” abridging freedom of speech, however, this does not apply to private businesses like Facebook. We’re not asking these companies to determine the boundaries of free speech across society. We just want them to be responsible on their platforms.
If a neo-Nazi comes goose-stepping into a restaurant and starts threatening other customers and saying he wants kill Jews, would the owner of the restaurant be required to serve him an elegant eight-course meal? Of course not! The restaurant owner has every legal right and a moral obligation to kick the Nazi out, and so do these internet companies.
Newer posts
Older posts











Socials & More