kottke.org posts about medicine
In the Atlantic, Ed Yong checks back in with the long-haulers, people who are still experiencing Covid-19 symptoms months after their initial infection. (Read his previous article from early June.)
Lauren Nichols has been sick with COVID-19 since March 10, shortly before Tom Hanks announced his diagnosis and the NBA temporarily canceled its season. She has lived through one month of hand tremors, three of fever, and four of night sweats. When we spoke on day 150, she was on her fifth month of gastrointestinal problems and severe morning nausea. She still has extreme fatigue, bulging veins, excessive bruising, an erratic heartbeat, short-term memory loss, gynecological problems, sensitivity to light and sounds, and brain fog. Even writing an email can be hard, she told me, “because the words I think I’m writing are not the words coming out.” She wakes up gasping for air twice a month. It still hurts to inhale.
As Yong says in a thread about the article: “The pandemic is going to create a large wave of chronically disabled people.” Once again for the people in the back: this is not just the flu. The flu does not incapacitate otherwise healthy people like this. I know at least two long-haulers personally and am astounded on a daily basis by how casually some Americans continue to regard Covid-19.
More than 90 percent of long-haulers whom Putrino has worked with also have “post-exertional malaise,” in which even mild bouts of physical or mental exertion can trigger a severe physiological crash. “We’re talking about walking up a flight of stairs and being out of commission for two days,” Putrino said. This is the defining symptom of myalgic encephalomyelitis, or chronic fatigue syndrome. For decades, people with ME/CFS have endured the same gendered gaslighting that long-haulers are now experiencing. They’re painfully familiar with both medical neglect and a perplexing portfolio of symptoms.
You can read Seabiscuit author Laura Hillenbrand’s excellent article on her chronic fatigue syndrome diagnosis and how difficult it is for people with chronic conditions like this to get the right diagnosis and to get family and friends to believe what’s going on.
Also, Yong should win all the awards this year for his pandemic coverage. It has been simply outstanding.
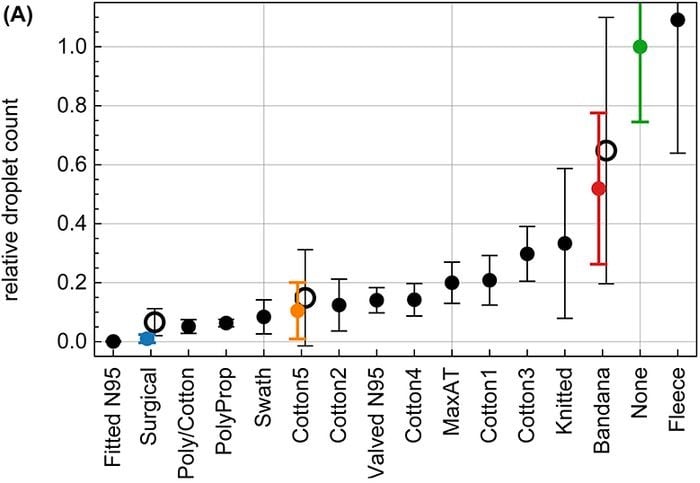
A new study on masks that measures the number of droplets emerging from the mouth during speech shows that properly fitted N95, surgical, and polypropylene masks are best, layered cotton masks are good, bandanas are not great, and neck gaiters may be worse than wearing no mask. Here’s a Washington Post article about the study.
I have some issues with this study — most masks were tested by only one speaker and mask materials were not identified precisely1 — but when combined with other studies about masks, it is clear that surgical masks or masks that are made with similar materials (polypropylene non-woven fabric) are what you want to shoot for, you want multiple layers for more protection (no single-layer microfiber gaiters), homemade cotton masks are pretty good (but would be better with a layer of polypropylene non-woven fabric), proper fit matters, and for god’s sake, stop wearing a bandana as a mask. Yes, bandanas are convenient, but you’re probably trading safety for that convenience, especially if you factor in the amount of time you’ll be wearing a mask over the next several months. A proper mask is going to protect you and your neighbors much more over the long haul — it’s just common sense at this point.
Re: the tested neck gaiter being worse than wearing no mask: the hypothesis is that the gaiter’s material splits large droplets into smaller ones, hence the higher count.
We noticed that speaking through some masks (particularly the neck fleece) seemed to disperse the largest droplets into a multitude of smaller droplets (see Supplementary Fig. S5), which explains the apparent increase in droplet count relative to no mask in that case. Considering that smaller particles are airborne longer than large droplets (larger droplets sink faster), the use of such a mask might be counterproductive.
Here’s what I’m taking away from this and other mask studies: wear the highest quality mask you can locate (multi-layered, incorporating surgical mask materials) that fits properly and, secondarily, is comfortable & convenient. For me, that’s a two-layer cotton mask (like these Vida masks) with an inserted layer of polypropylene non-woven fabric. An N95 would be much better in terms of efficacy, but it’s overkill in most situations (particularly here in VT, where rates continue to be low) and is difficult to fit properly and quickly. (via @EricTopol)
Update: Slate’s Susan Matthews goes into more detail about the problems with this study and the conclusions that others are drawing from it.
The purpose of the research was to establish that the testing method worked in principle-not to come up with meaningful or accurate verdicts about particular masks.
But she also concludes (correctly, in my mind):
Should you think twice about wearing just a gaiter inside, in close proximity to other people? Yeah, a fitted mask is probably better. But you didn’t need this study to tell you that.
(via @BrianDau)
Update: But interesting to note that in this test, scarves, bandanas, and microfiber neck gaiters came in last.
The American system of law enforcement is so deeply embedded into our national psyche that if you find the idea of defunding or abolishing the police challenging, I don’t blame you. But imagine calling an ambulance because a loved one was having trouble breathing or was suffering a stroke and, instead of the expected trained paramedics, a man with a gun showed up. Not great, right? As Jamie Ford explains in this thread, that was not unusual in America until recently.
Until the 70s, ambulance services were generally run by local police and fire departments. There was no law requiring medical training beyond basic first-aid and in many cases the assignment of ambulance duty was used as a form of punishment.
As you can imagine, throwing people with medical emergencies into the back of a paddy wagon produced less than spectacular health outcomes. Now imagine how much worse it became when disgruntled white police officers were demoted to ambulance duty in black neighborhoods.
From Kevin Hazzard’s The First Responders:
Emergency care was mostly a transportation industry, focused on getting patients to hospitals, and it was dominated by two groups: funeral homes and police departments. Call the local authorities for help and you’d likely get morticians in a hearse or cops in a paddy wagon. If you received any treatment en route to the hospital — and most likely you did not — it wouldn’t be very good. At best, one of the people helping may have taken a first-aid course. At worst, you’d ride alone in the back, hoping, if you were conscious, that you’d survive.
Pittsburgh’s Freedom House Ambulance Service changed all that, ushering in a new era of much improved medical care for communities around the US.
Together the two men hashed out a plan: Hallen would raise the money, Safar would contribute his medical expertise, and together they would design advanced ambulances and teach paramedics to provide care on the scene of an accident or emergency. It would be a pioneering medical effort, and Hallen, who was white, suggested another first. The Falk Fund was committed to mitigating racism, and Hallen wanted to staff the service with young black men from the Hill. He hoped that empowering individuals long deemed unemployable would be a source of pride in the black community, a symbol of equality, and a signal that bigoted notions about the black people of Pittsburgh standing in their own way were nonsense.
To help with recruitment, Hallen and Safar partnered with an organization called Freedom House Enterprises, a nonprofit dedicated to establishing and supporting black-run businesses in the city. Freedom House handled staffing for the fledgling ambulance service and recruited the first class of paramedics, including Vietnam veterans and men with criminal records.
So this is a great instance in which armed and untrained police officers have been relieved of a particular responsibility and replaced with specially trained personnel, resulting in a greatly improved outcome for members of the community. If you want other examples, just think about how odd, unhelpful, and dangerous it would be for our communities if the police showed up — armed with a loaded weapon — to collect your garbage, to put out fires, to inspect restaurants, to fix potholes, or to deliver the mail. No, we have sanitation workers, firefighters, public health inspectors, municipal maintenance workers, and postal workers to do these jobs — and they’re all trained in the ins and outs of their particular disciplines.
With these examples in mind, instead of armed personnel handling a wide variety of situations for which they are often not trained, it becomes easier to imagine traffic patrols conducting transportation safety stops, social workers responding to domestic disputes, special crisis centers assisting rape victims, mental health counselors helping people behaving erratically in public, housing guides finding homeless folks a place to stay, student safety coaches helping struggling students navigate school, unarmed personnel responding to property crime, and drug addiction counselors helping drug users stay safe. These are all areas where American communities have applied policing by default, like a flimsy bandaid. It’s ineffective, expensive, and dangerous, and communities should think seriously about supporting and funding alternatives that will be more effective, cheaper, safer, and produce better outcomes for everyone.
Update: See also (hear also?) 99% Invisible’s episode on the Freedom House Ambulance Service.
Kristen McConnell writing for The Atlantic: I’m a Nurse in New York. Teachers Should Do Their Jobs, Just Like I Did.
So I can understand that teachers are nervous about returning to school. But they should take a cue from their fellow essential workers and do their job. Even people who think there’s a fundamental difference between a nurse and a teacher in a pandemic must realize that there isn’t one between a grocery-store worker and a teacher, in terms of obligation. People who work at grocery stores in no way signed up to expose themselves to disease, but we expected them to go to work, and they did. If they had not, society would have collapsed. What do teachers think will happen if working parents cannot send their children to school? Life as we know it simply will not go on.
Oh yes, that is a totally awesome thing our brave grocery store workers did for us out of a sense of obligation and not because their choice was between risking their health and losing their job in a country with a terrible social safety net. But let’s leave that to one side for a second.
I think many more people would support (and indeed rapturously welcome) kids going back to school if a) there were many fewer cases of Covid-19 in the US, b) if the federal and state governments were doing more testing, tracing, and isolation & support of those who test positive, c) if there was more support for parents, and especially low-income folks, with other options around education and childcare (more on that below), and d) if the mask issue wasn’t so contentious in some parts of the country. Oh and don’t forget that even before any of this happened, teachers regularly used their own money and held online fundraisers to buy necessary school supplies for their classrooms.
Blaming teachers for not wanting to go back to work because their country and communities can’t or won’t do the hard work of making it safe is ridiculous. It’s not fair to ask them to do their part when others with greater responsibility to act are not. Someone has been watching too many war movies where soldiers dying due to the negligence, incompetence, or bad intentions of their superiors is played off as patriotic service & bravery instead of murder.
And this…this is just flat out false:
(And parents who want their children to stay home have that option, whether through homeschooling or continued remote learning.)
Rich people with reliable internet access and extra computers lying around have that option, and it’s a terrible option if those parents work (especially if they’re single parents). A huge chunk of America does not.1 If, by some miracle, the federal government started paying people to stay home from work to help their kids with school, gave everyone a laptop stipend (as well as enough money so that kids have access to meals that they might usually get through school programs), and ensured internet access to those who don’t have it, that statement would be closer to the truth. As long as we’re waving magic wands, I would like a chocolate pony and a peanut butter unicorn.
I would have been far more sympathetic to McConnell’s case had she made a convincing argument that school is so essential to children that it’s worth the risk to them, their teachers, and their families, that schools and governments are doing the right things to ensure the safety of their students and staff, and that Covid-19 is coming under control in the United States. But she did not.
Update: Sarah Jones rebuts McConnell’s argument for New York magazine: Teachers Aren’t Sacrificial Lambs. No Essential Worker Is.
The idea that remote work and home education don’t qualify as doing one’s part for society is so pernicious that it nearly distracts from McConnell’s core argument, which is both simple and widespread: If work is essential, it must also be sacrificial. That argument is worth examining, not least because it’s likely to reappear as parents cope with another semester at home. McConnell has taken a view expressed most commonly in the pandemic policies of certain large corporations and extended it to teachers. The same thread is visible both in Amazon’s failure to get enough masks to workers and to ensure social-distancing in warehouses and in the insistence that teachers should head back into classrooms, whatever the risk.
I also had a bunch of mail in my inbox this morning, both from teachers and healthcare professionals, poking holes in this poorly argued piece. The Atlantic’s coverage of the pandemic has been outstanding, but this article was just not very good — a rare misfire. (via @zidaya)
From We Can Eliminate Covid-19 if We Want To by Andy Slavitt:
We can virtually eliminate the virus any time we decide to. We can be back to a reasonably normal existence: schools, travel, job growth, safer nursing homes and other settings. And we could do it in a matter of weeks. If we want to.
Take New Zealand. With its fancy curve and life back to normal. Why can’t we? Not fair, you say. It’s an island nation. Okay. What about Germany? Not an island nation, large, growing diversity. Don’t like that comparison? What about countries that have been in big trouble? There’s Italy, France, and Spain. Those countries had it reasonably bad the same time we did. In fact, pick virtually any country you want.
But don’t tell me the United States can’t take action if we want to. And we can’t face the families of 150,000 people who didn’t have to die and tell them this had to happen. And I think it’s why our national political leaders won’t go near these families and the grieving process.
The good news — and it is good news — is we are always four to six weeks from being able to do what countries around the world have done.
I know this article is supposed to be hopeful and optimistic, but people have known what to do about Covid-19 since at least March. Instead the United States has not done it and indeed has done mostly the opposite. The “we” that are supposed to decide to lead this effort won’t because they don’t want to put in the work (it’s easier to blame the virus, Democrats, and China), they don’t want to just give money to people to stay home (a huge no-no for Republicans), and they don’t care that much about who is dying (urbanites, low-income, the elderly, Black & brown people).
As long as Republicans control the Senate and White House, the current scattershot approach of each state/county/city/person deciding what is best (or most in their self-interest) is what we’re stuck with. Treatments will improve, vaccines will be developed, many people will do the right thing and mostly stay home for many more months (sacrificing their mental health to do so), and Covid-19 will eventually come under control, but hundreds of thousands more people will die, many more will recover but carry chronic illnesses for years, vital years of the survivors’ lives will have been lost, and we will collectively grieve these losses for generations.
The Atlantic’s Sarah Zhang has A Vaccine Reality Check for us.
Biologically, a vaccine against the COVID-19 virus is unlikely to offer complete protection. Logistically, manufacturers will have to make hundreds of millions of doses while relying, perhaps, on technology never before used in vaccines and competing for basic supplies such as glass vials. Then the federal government will have to allocate doses, perhaps through a patchwork of state and local health departments with no existing infrastructure for vaccinating adults at scale. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which has led vaccine distribution efforts in the past, has been strikingly absent in discussions so far — a worrying sign that the leadership failures that have characterized the American pandemic could also hamper this process. To complicate it all, 20 percent of Americans already say they will refuse to get a COVID-19 vaccine, and with another 31 percent unsure, reaching herd immunity could be that much more difficult.
I am the least anti-vaxxer person in the world, but I have to say that getting a vaccine for Covid-19 that was rushed through trials in time for the election (October surprise!) and signed off by a Trump administration that has completely politicized science does not sound like something I want to go near. Which, for me personally, is a really really depressing thing to even think.
Update: I got a lot of flack for suggesting that I’d be skeptical of a Trump-approved vaccine rushed to market in time for the election (a very specific set of circumstances). But his buddy Putin is attempting something similar in Russia (skipping phase 3 trials), so if you don’t think Trump can try to bully the FDA and CDC into signing off on a vaccine that hasn’t been fully tested — perhaps made by a company whose CEO has donated millions to a Trump SuperPAC? — in order to salvage his reelection chances, I suggest that you haven’t paying proper attention over the past 4 years.
Update: A poll suggests that many Americans across the political spectrum are worried about a politicized FDA being forced to approve a Covid-19 vaccine before it’s adequately tested.
Seventy-eight percent of Americans worry the Covid-19 vaccine approval process is being driven more by politics than science, according to a new survey from STAT and the Harris Poll, a reflection of concern that the Trump administration may give the green light to a vaccine prematurely.
The response was largely bipartisan, with 72% of Republicans and 82% of Democrats expressing such worries, according to the poll, which was conducted last week and surveyed 2,067 American adults.
The sentiment underscores rising speculation that President Trump may pressure the Food and Drug Administration to approve or authorize emergency use of at least one Covid-19 vaccine prior to the Nov. 3 election, but before testing has been fully completed.
From Dr. Anna DeForest, a devastating article — a prose poem almost — in The New England Journal of Medicine: The New Stability.
This is the day you start to turn. What we suck up from your lungs turns frothy pink and then the frank red of blood. We don’t know if your heart is finally failing or if the virus has destroyed so much tissue that this is necrosis, hemorrhaged in your lungs. There are tests, but no one willing to run them — you are too sick, and you have never cleared the virus. No one would ever want to be what you are now: a hazard, a threat, a frightening object on the edge of death. We try not to touch you. We construct our plans for saving you around staying as far away from you as possible.
I tell your husband about the blood. It’s true that nothing else has changed: your struggling lungs, with help, still take in air, your heart, with help, still brags along. “But she is stable,” he asks, barely a question. Why do I lie? “Yes,” I say, “for now.”
DeForest wrote this in early May as Covid-19 cases peaked at her hospital in New Haven. The country and its leaders ignored this and now cases are spiking in many hospitals all around the country now. Just some sniffles, though, nothing to bother anyone about.
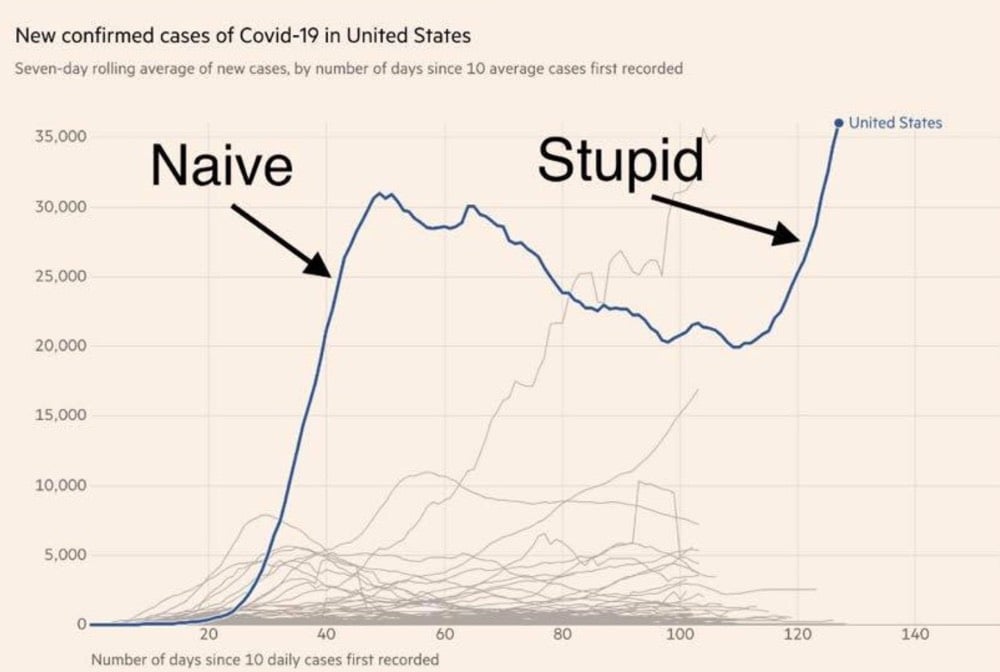
The director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, Anthony Fauci, told a Senate committee today that the US could be heading towards 100,000 new reported cases of Covid-19 per day. 100,000 cases per day. Yesterday the US recorded about 40,000 new cases.
“It is going to be very disturbing, I will guarantee you that,” he said.
“What was thought to be unimaginable turns out to be the reality we’re facing right now,” Fauci said, adding that “outbreaks happen, and you have to deal with them in a very aggressive, proactive way.”
Fewer than 20 countries have recorded more than 100,000 cases in total. Canada, for instance, has confirmed about 106,000 Covid-19 cases since the outbreak began.
Public health and infectious diseases experts, who have been gravely concerned about the way the U.S. response has unfolded, concurred with Fauci’s assessment.
Bars and restaurants are reopening around the country without any serious effort to test/trace/isolate/support. In the absence of strident guidance from the federal government, people are worrying less about social distancing and wearing masks to protect others. As this guy says, it’s just a matter of math:
“It’s unfortunately just a simple consequence of math plus a lack of action,” said Marm Kilpatrick, an infectious diseases dynamics researcher at the University of California, Santa Cruz. “On the one hand it comes across as ‘Oh my God, 100,000 cases per day!’ But then if you actually look at the current case counts and trends, how would you not get that?”
Absolutely nothing has changed about the virus, so its spread is determined by pretty simple exponential growth.
Limiting person-to-person exposure and decreasing the probability of exposures becoming infections can have a huge effect on the total number of people infected because the growth is exponential. If large numbers of people start doing things like limiting travel, cancelling large gatherings, social distancing, and washing their hands frequently, the total number of infections could fall by several orders of magnitude, making the exponential work for us, not against us. Small efforts have huge results.
We’ve known for months (and epidemiologists and infectious disease experts have known for their entire careers) what works and yet the federal government and many state governments have not listened and, in some cases, have actively suppressed use of such measures. So the pandemic will continue to escalate in the United States until proper measures are put in place by governments and people follow them. The virus will not change, the mathematics will not change, so we must.
Graph at the top of the post via Rishi Desai.
In The Price of Isolation for Rolling Stone, Alex Morris writes about how trends toward increasing social isolation in America left us ill-prepared to face weeks and months of time by ourselves during the pandemic. Studies have shown that humans in isolation are less healthy and less able to fight off disease than when other humans are around. This part in particular really really resonated with me:
Sometimes, though, the body can be tricked. When Cole and his colleagues started looking for ways to combat the physical effects of loneliness, they didn’t find that positive emotions made a difference at all. But one thing did: “It was something called eudaimonic well-being, which is a sense of purpose and meaning, a sense of a commitment to some kind of self-transcendent goal greater than your own immediate self-gratification. People who have a lot of connection to some life purpose? Their biology looked great.” Even when researchers compared lonely people with purpose to social butterflies without it, purpose came out on top. In other words, it’s possible when we’re doing things to better our society, the body assumes there’s a society there to better. We’re technically alone, but it doesn’t feel that way.
Which has profound implications in the moment in which we currently find ourselves, a moment when the physical isolation and disconnection the virus has inflicted is now layered over the clear divisions and systemic inequities that have always plagued our country. In the midst of our solitude, we’ve been confronted with the terrible knowledge that people of color are dying of the virus at the highest rates and that 40 percent of families making less than $40,000 a year have lost their livelihoods. We’ve been confronted with the killings of Ahmaud Arbery, Breonna Taylor, and George Floyd. We’ve been confronted with the lie that the virus is a great equalizer. We’ve witnessed the many ways it isn’t.
See also We’re All Lonely Together and An Epidemic of Middle-aged Male Loneliness.
In 1854, Dr. John Snow produced a map of a London cholera outbreak which showed deaths from the disease concentrated around a water pump on Broad Street. The prevailing view at the time was that cholera spread through dirty air, but Snow hypothesized that it was actually spread through water and constructed this early medical data visualization to help prove it.
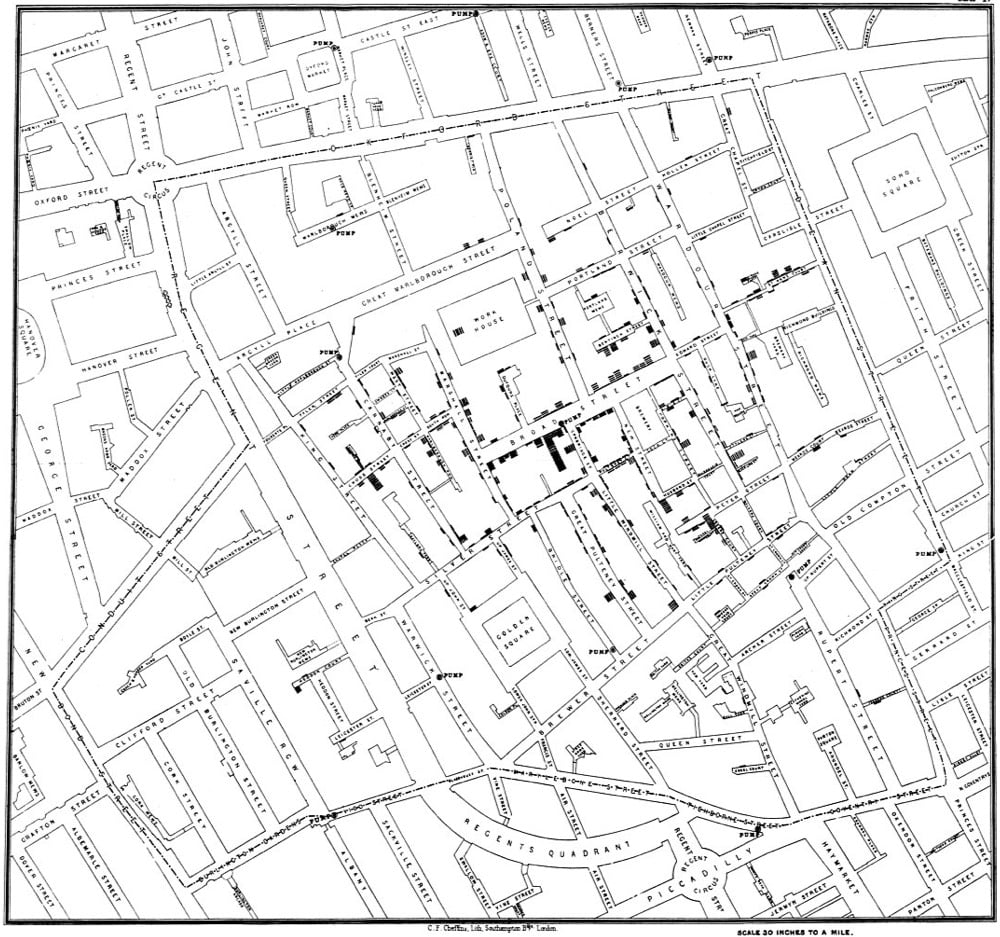
Through a mix of personal interviews, clever detective work, and data analysis that included tables and a famous map, Snow managed to stop the outbreak and convince local public health officials, eventually, that cholera could be transmitted through water, not a miasma. Since his breakthrough study, the map has become an iconic piece of epidemiological history, as an illustration of keen detective work, analysis, and visual representation with a map that, even today, tells a story.
Aside from the cluster of deaths around the pump (which could be argued were the result of a miasma cloud and not contaminated water), stories of nearby people who didn’t get sick (brewers who drank the beer they produced rather than well water, people in buildings with their own wells) and far away people who died because they had drunk water from the well were also essential in proving his theory:
I was informed by this lady’s son that she had not been in the neighbourhood of Broad Street for many months. A cart went from broad Street to West End every day and it was the custom to take out a large bottle of the water from the pump in Broad Street, as she preferred it. The water was taken on Thursday 31st August., and she drank of it in the evening, and also on Friday. She was seized with cholera on the evening of the latter day, and died on Saturday
You can read more about John Snow and how his map changed science and medicine in Steven Johnson’s excellent Ghost Map.
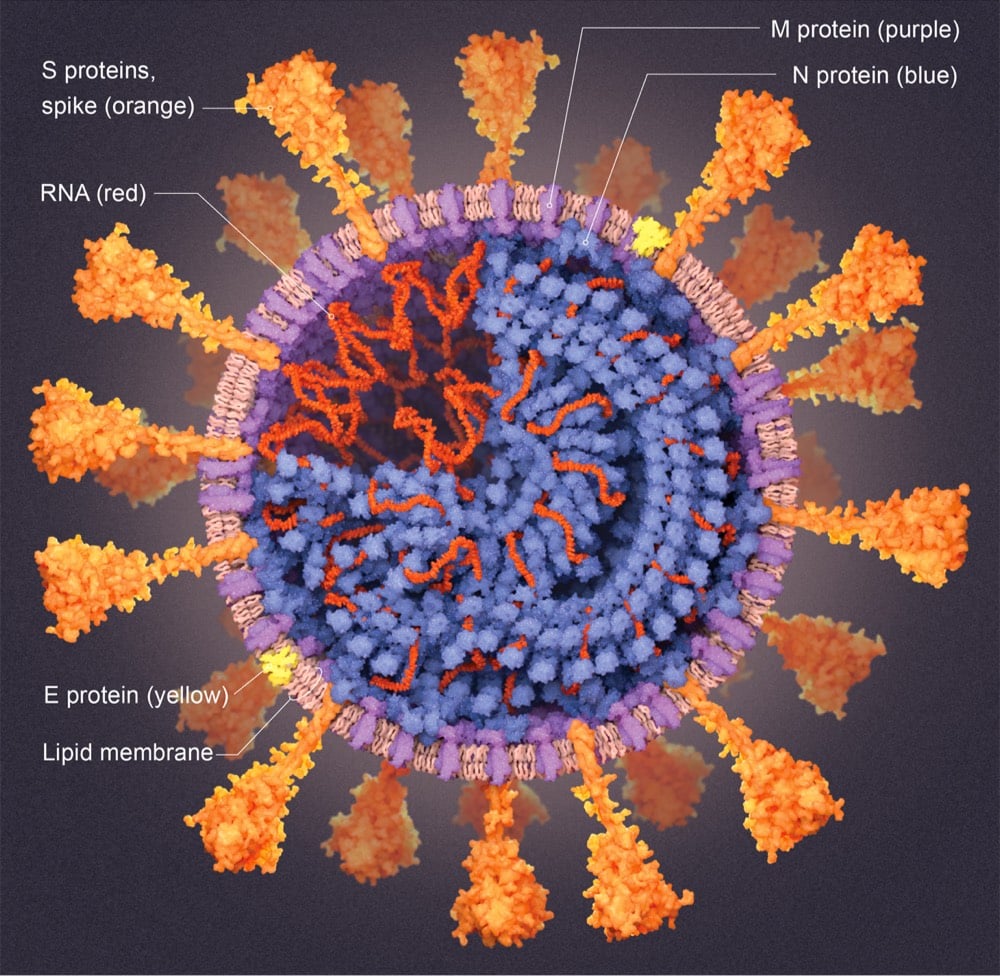
For its July 2020 issue, Scientific American has published A Visual Guide to the SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus detailing what scientists have learned about this tiny menace that’s brought our world to a halt.
In the graphics that follow, Scientific American presents detailed explanations, current as of mid-May, into how SARS-CoV-2 sneaks inside human cells, makes copies of itself and bursts out to infiltrate many more cells, widening infection. We show how the immune system would normally attempt to neutralize virus particles and how CoV-2 can block that effort. We explain some of the virus’s surprising abilities, such as its capacity to proofread new virus copies as they are being made to prevent mutations that could destroy them. And we show how drugs and vaccines might still be able to overcome the intruders.
In a his book out today, Which Country Has the World’s Best Health Care?, oncologist & bioethicist Ezekiel Emanuel compares the outcomes of several countries’ health care systems.
The US spends more than any other nation, nearly $4 trillion, on healthcare. Yet, for all that expense, the US is not ranked #1 — not even close.
In Which Country Has the World’s Best Healthcare? Ezekiel Emanuel profiles 11 of the world’s healthcare systems in pursuit of the best or at least where excellence can be found. Using a unique comparative structure, the book allows healthcare professionals, patients, and policymakers alike to know which systems perform well, and why, and which face endemic problems. From Taiwan to Germany, Australia to Switzerland, the most inventive healthcare providers tackle a global set of challenges — in pursuit of the best healthcare in the world.
In his ranking of 11 countries profiled, China and the United States are, respectively, dead last and second-to-last in providing health care for their citizens. In the case of the United States at least, that failure is on display with our response to the Covid-19 pandemic.
Several countries have been celebrated for their success in curtailing the Covid-19 pandemic — Iceland, New Zealand, Mongolia, Hong Kong, Taiwan — but Vietnam, a nation of 95 million people that borders China, has recorded only 334 total infections and 0 deaths. 0 deaths. They are currently on a 61-day streak without a single community transmission. (For reference, the US has recorded 2.1 million cases and more than 115,000 deaths with just 3.4 times the population of Vietnam.)
How have they done it? They acted early and aggressively.
Experts say experience dealing with prior pandemics, early implementation of aggressive social distancing policies, strong action from political leaders and the muscle of a one-party authoritarian state have helped Vietnam.
“They had political commitment early on at the highest level,” says John MacArthur, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s country representative in neighboring Thailand. “And that political commitment went from central level all the way down to the hamlet level.”
With experience gained from dealing with the 2003 SARS and 2009 H1N1 pandemics, Vietnam’s government started organizing its response in January — as soon as reports began trickling in from Wuhan, China, where the virus is believed to have originated. The country quickly came up with a variety of tactics, including widespread quarantining and aggressive contact tracing. It has also won praise from the World Health Organization and the CDC for its transparency in dealing with the crisis.
From the BBC:
Vietnam enacted measures other countries would take months to move on, bringing in travel restrictions, closely monitoring and eventually closing the border with China and increasing health checks at borders and other vulnerable places.
Schools were closed for the Lunar New Year holiday at the end of January and remained closed until mid-May. A vast and labour intensive contact tracing operation got under way.
“This is a country that has dealt with a lot of outbreaks in the past,” says Prof Thwaites, from Sars in 2003 to avian influenza in 2010 and large outbreaks of measles and dengue.
“The government and population are very, very used to dealing with infectious diseases and are respectful of them, probably far more so than wealthier countries. They know how to respond to these things.”
By mid-March, Vietnam was sending everyone who entered the country - and anyone within the country who’d had contact with a confirmed case — to quarantine centres for 14 days.
Costs were mostly covered by the government, though accommodation was not necessarily luxurious. One woman who flew home from Australia — considering Vietnam a safer place to be - told BBC News Vietnamese that on their first night they had “only one mat, no pillows, no blankets” and one fan for the hot room.
Forced bussing to quarantine centers in the US, could you even imagine? Better that hundreds of thousands of people die, I guess.
The Vietnamese health system also implemented aggressive contact tracing:
Authorities rigorously traced down the contacts of confirmed coronavirus patients and placed them in a mandatory two-week quarantine.
“We have a very strong system: 63 provincial CDCs (centers for disease control), more than 700 district-level CDCs, and more than 11,000 commune health centers. All of them attribute to contact tracing,” said doctor Pham with the National Institute of Hygiene and Epidemiology.
A confirmed coronavirus patient has to give health authorities an exhaustive list of all the people he or she has met in the past 14 days. Announcements are placed in newspapers and aired on television to inform the public of where and when a coronavirus patient has been, calling on people to go to health authorities for testing if they have also been there at the same time, Pham said.
More from Axios and The Guardian.
The conclusion from a recent paper in the Proceedings of the Royal Society A:
We conclude that facemask use by the public, when used in combination with physical distancing or periods of lock-down, may provide an acceptable way of managing the COVID-19 pandemic and re-opening economic activity. These results are relevant to the developed as well as the developing world, where large numbers of people are resource poor, but fabrication of home-made, effective facemasks is possible. A key message from our analyses to aid the widespread adoption of facemasks would be: ‘my mask protects you, your mask protects me’.
From a Reuters report on the paper:
The research, led by scientists at the Britain’s Cambridge and Greenwich Universities, suggests lockdowns alone will not stop the resurgence of the new SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus, but that even homemade masks can dramatically reduce transmission rates if enough people wear them in public.
“Our analyses support the immediate and universal adoption of face masks by the public,” said Richard Stutt, who co-led the study at Cambridge.
A pair of recent papers used the geographic differences in mask usage in Germany to gauge the effectiveness of masks in preventing the spread of Covid-19. Face Masks Considerably Reduce COVID-19 Cases in Germany:
We use the synthetic control method to analyze the effect of face masks on the spread of Covid-19 in Germany. Our identification approach exploits regional variation in the point in time when face masks became compulsory. Depending on the region we analyse, we find that face masks reduced the cumulative number of registered Covid-19 cases between 2.3% and 13% over a period of 10 days after they became compulsory. Assessing the credibility of the various estimates, we conclude that face masks reduce the daily growth rate of reported infections by around 40%.
And Compulsory face mask policies do not affect community mobility in Germany suggests that people don’t go out more or “feel invincible” when they’re wearing masks:
We use anonymised GPS data from Google’s Location History feature to measure daily mobility in public spaces (groceries and pharmacies, transport hubs and workplaces). We find no evidence that compulsory face mask policies affect community mobility in public spaces in Germany. The evidence provided in this paper makes a crucial contribution to ongoing debates about how to best manage the COVID-19 pandemic.
And these are just from the last few days. Why WHY WHY!!!! are we still talking about this? There’s no credible evidence that wearing a mask is harmful, so at worse it’s harmless. If there’s like a 1-in-10 chance that masks are somewhat helpful — and the growing amount of research suggests that both 1-in-10 and “somewhat helpful” are both understatements — isn’t it worth the tiny bit of effort to wear one and help keep our neighbors safe from potential fucking death? Just in case?
I mean, look at where we are as a country right now. Most of the US is reopening while the number of infections continue to rise. Testing is still not where it needs to be in many areas. Tracing and isolation are mostly not happening. According to epidemiologists, those are the minimum things you need to do to properly contain a pandemic like this. Maybe if you’re Iceland you can pooh pooh the efficacy of masks because you test/trace/isolated to near-perfection, but if you’re going to half-ass it like the US has chosen to do, then wearing masks under semi-lockdown conditions is all we have left! Can we do the bare minimum that is asked of us?
Update: And some anecdotal evidence from Missouri: two hairstylists saw 140 clients while symptomatic last month and it resulted in zero infections. Both the hairstylists and their clients wore masks and took other precautions (staggered appointments, chairs spaced apart).
Update: I deleted a reference to this paper that many epidemiologists et al. have flagged as problematic (see here, here, and here for instance). (via @harrislapiroff)
The Masks Masquerade by Nassim Nicholas Taleb is worth a read.
“Libertarians” (in brackets) are resisting mask wearing on grounds that it constrains their freedom. Yet the entire concept of liberty lies in the Non-Aggression Principle, the equivalent of the Silver Rule: do not harm others; they in turn should not harm you. Even more insulting is the demand by pseudolibertarians that Costco should banned from forcing customers to wear mask — but libertarianism allows you to set the rules on your own property. Costco should be able to force visitors to wear pink shirts and purple glasses if they wished.
Note that by infecting another person you are not infecting just another person. You are infecting many many more and causing systemic risk.
Wear a mask. For the Sake of Others.
And finally, obviously, if wearing a mask is not advisable for you — for a genuine medical reason or if it makes you look dangerous to a racist policing system for instance — then you shouldn’t wear one! But the vast majority of us should be able to manage it.
Update: A study in Health Affairs analyzing the infection rates in US states with face mask mandates versus those without finds that a mandate was associated with a decline in the Covid-19 growth rate (italics mine).
Mandating face mask use in public is associated with a decline in the daily COVID-19 growth rate by 0.9, 1.1, 1.4, 1.7, and 2.0 percentage points in 1-5, 6-10, 11-15, 16-20, and 21+ days after signing, respectively. Estimates suggest as many as 230,000-450,000 COVID-19 cases possibly averted By May 22, 2020 by these mandates. The findings suggest that requiring face mask use in public might help in mitigating COVID-19 spread.
In a comparison among countries, those where people wore masks early fared much better than those where people didn’t. This is a pretty stark difference:
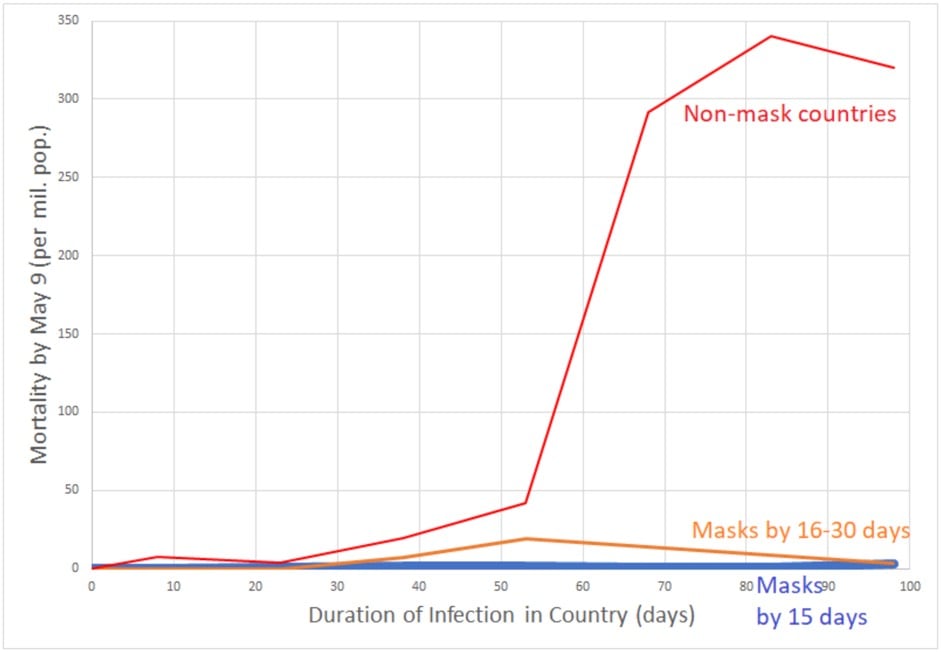
And this study noted that Google search volume of people searching for masks in various countries correlated with the infection rate — in general, the earlier the search volume increased in a given country, the fewer infections recorded in that country.
Update: A list of 70 scientific studies, dating all the way back to 2003, that support the wearing of face masks to prevent disease spread.
Bill Nye recently did a quick mask demonstration featuring a candle to show how effective homemade cloth masks are at blocking exhaled breath. He calls wearing a mask in public to protect other people “literally a matter of life and death”.
Stewart Reynolds shares some reasons to not wear a face mask, including selfish syndrome and chronic dickishness.
And this is a sad and all-too-typical American story in four parts. April: I’m not buying a mask; June: crowded pool party; July: complaining about being sick followed by an obituary. We need to fix this, now. People should not be dying like this — this is a 100% preventable death.
Update: The most recent version of an ongoing review of scientific studies about face mask efficacy was recently published online. From the abstract:
We recommend that public officials and governments strongly encourage the use of widespread face masks in public, including the use of appropriate regulation.
In The Atlantic, epidemiologists Julia Marcus and Gregg Gonsalves explain why public health officials are not being hypocritical in their support of the antiracism protests around the country.
At its core, the argument being leveled against public-health experts is that the reason for the protests shouldn’t matter. The coronavirus doesn’t care whether it’s attending an anti-lockdown protest or an anti-racism one. But these two kinds of protests are not equivalent from a public-health perspective. Some critics might argue that the anti-lockdown protests promoted economic activity, which can help stave off the health implications of poverty. (On this count, public-health experts were ahead of the curve: Many — including one of us — were advocating for a massive infusion of assistance to individual Americans as early as March.) But these protests were organized by pro-gun groups that believe the National Rifle Association is too compromising on gun safety. Egged on by the president to “save your great 2nd Amendment,” anti-lockdown protesters stormed government buildings with assault rifles and signs reading COVID-19 IS A LIE. The anti-lockdown demonstrations were explicitly at odds with public health, and experts had a duty to oppose them. The current protests, in contrast, are a grassroots uprising against systemic racism, a pervasive and long-standing public-health crisis that leads to more than 80,000 excess deaths among black Americans every year.
If “conservative commentators” cared at all about keeping people safe from Covid-19 infection, they would have denounced the I-Need-A-Haircut protests as reckless and they didn’t. Instead, they engage in these bad faith arguments that are just designed to stir up outrage.
Gonsalves wrote a thread on Twitter a few days ago that’s relevant here as well.
The risk to all of us was inflamed by an absolute decision at the highest levels that this epidemic was not worth an all-out, coordinated, comprehensive national mobilization. It took weeks for the President to even agree that the epidemic wouldn’t go away on its own.
The US, the richest nation in the world, then couldn’t get it together to scale-up the number of tests we needed to understand what was going on in our communities with SARS-COV-2, and in the end said it was up to the states to figure it all out.
And then this is the last word as far as I’m concerned:
We’ve all been put at far more jeopardy during this pandemic by our political leaders than by the people on the streets over the past week or so.
One of the countries with the best response to Covid-19 has been Iceland. The country didn’t lockdown nor do many people wear masks, but they have virtually eliminated the virus through a vigorous program of test, trace, and isolate that was coordinated by public-health authorities. Iceland’s numbers were high in the beginning (the virus was carried into the country from people returning from vacation) but they acted quickly and aggressively — Elizabeth Kolbert has the story for the New Yorker.
Möller pulled up a series of graphs and charts on her laptop. These showed that, per capita, Iceland had had more COVID-19 cases than any other Scandinavian country, and more than even Italy or Britain. There was an outbreak in a nursing home in the town of Bolungarvík, in northwestern Iceland, and one in the Westman Islands, an archipelago off the southern coast, which seemed to have started at a handball game. (In Europe, handball is a team sport that’s sort of a cross between basketball and soccer.)
“The numbers in the beginning were terrible,” Möller said. She attributed the country’s success in bringing the caseload down in part to having got an early start. The “trio,” along with officials from Iceland’s university hospital, had begun meeting back in January. “We saw what was going on in China,” she recalled. “We saw the pictures of people lying dead in emergency departments, even on the street. So it was obvious that something terrible was happening. And, of course, we didn’t know if it would spread to other countries. But we didn’t dare take the chance. So we started preparing.” For example, it was discovered that the country didn’t have enough protective gear for its health-care workers, so hospital officials immediately set about buying more.
The Atlantic’s Ed Yong interviewed several people who, like thousands of others around the world, have been experiencing symptoms of Covid-19 for months now, indicating that the disease is chronic for some. Thousands Who Got COVID-19 in March Are Still Sick:
I interviewed nine of them for this story, all of whom share commonalities. Most have never been admitted to an ICU or gone on a ventilator, so their cases technically count as “mild.” But their lives have nonetheless been flattened by relentless and rolling waves of symptoms that make it hard to concentrate, exercise, or perform simple physical tasks. Most are young. Most were previously fit and healthy. “It is mild relative to dying in a hospital, but this virus has ruined my life,” LeClerc said. “Even reading a book is challenging and exhausting. What small joys other people are experiencing in lockdown-yoga, bread baking-are beyond the realms of possibility for me.”
One of those who has been sick for months is Paul Garner, a professor of infectious diseases:
It “has been like nothing else on Earth,” said Paul Garner, who has previously endured dengue fever and malaria, and is currently on day 77 of COVID-19. Garner, an infectious-diseases professor at the Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine, leads a renowned organization that reviews scientific evidence on preventing and treating infections. He tested negative on day 63. He had waited to get a COVID-19 test partly to preserve them for health-care workers, and partly because, at one point, he thought he was going to die. “I knew I had the disease; it couldn’t have been anything else,” he told me. I asked him why he thought his symptoms had persisted. “I honestly don’t know,” he said. “I don’t understand what’s happening in my body.”
Garner wrote about his experience for BMJ.
The illness went on and on. The symptoms changed, it was like an advent calendar, every day there was a surprise, something new. A muggy head; acutely painful calf; upset stomach; tinnitus; pins and needles; aching all over; breathlessness; dizziness; arthritis in my hands; weird sensation in the skin with synthetic materials. Gentle exercise or walking made me worse — I would feel absolutely dreadful the next day. I started talking to others. I found a marathon runner who had tried 8 km in her second week, which caused her to collapse with rigors and sleep for 24 hours. I spoke to others experiencing weird symptoms, which were often discounted by those around them as anxiety, making them doubt themselves.
We still have no idea what the long-term effects of this disease are going to be. But it is definitely not the flu. And I remain unwilling to risk myself or my family getting it.
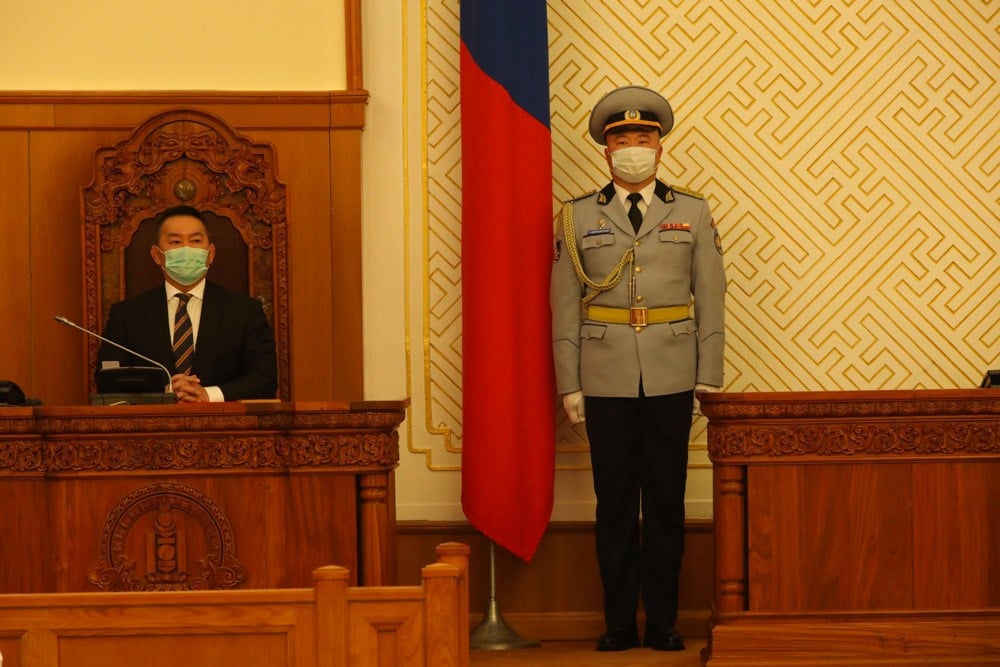

Several countries have had solid responses to the Covid-19 pandemic: Taiwan, South Korea, New Zealand, and Hong Kong. But Indi Samarajiva thinks we should be paying much more attention to Mongolia, a country of 3.17 million people where no one has died and no locally transmitted cases have been reported.1 Let’s have that again: 3.17 million people, 0 local cases, 0 deaths. How did they do it? They saw what was happening in Wuhan, coordinated with the WHO, and acted swiftly & decisively in January.
Imagine that you could go back in time to January 23rd with the horse race results and, I dunno, the new iPhone. People believe you. China has just shut down Hubei Province, the largest cordon sanitaire in human history. What would you scream to your leaders? What would you tell them to do?
You’d tell them that this was serious and that it’s coming for sure. You’d tell them to restrict the borders now, to socially distance now, and to get medical supplies ready, also now. You’d tell them to react right now, in January itself. That’s 20/20 hindsight.
That’s exactly what Mongolia did, and they don’t have a time machine. They just saw what was happening in Hubei, they coordinated with China and the WHO, and they got their shit together fast. That’s their secret, not the elevation. They just weren’t dumb.
When you go to World In Data’s Coronavirus Data Explorer and click on “Mongolia” to add their data to the graph, nothing happens because they have zero reported cases and zero deaths. They looked at the paradox of preparation — the idea that “when the best way to save lives is to prevent a disease rather than treat it, success often looks like an overreaction” — and said “sign us up for the overreacting!”
Throughout February, Mongolia was furiously getting ready - procuring face masks, test kits, and PPE; examining hospitals, food markets, and cleaning up the city. Still no reported cases. Still no let-up in readiness. No one was like “it’s not real!” or “burn the 5G towers!”
The country also suspended their New Year celebrations, which are a big deal in Asia. They deployed hundreds of people and restricted intercity travel to make sure, though the public seemed to broadly support the move.
Again — and I’ll keep saying this until March — there were still NO CASES. If you want to know how Mongolia ended up with no local cases, it’s because they reacted when there were no local cases. And they kept acting.
For example, when they heard of a case across the border (ie, not in Mongolia) South Gobi declared an emergency and put everyone in masks. The center also shut down coal exports — a huge economic hit, which they took proactively.
As you can see, at every turn they’re reacting like other countries only did when it was too late. This looked like an over-reaction, but in fact, Mongolia was always on time.
I have to tell you true: I got really upset reading this. Like crying and furious. The United States could have done this. Italy could have done this. Brazil could have done this. Sweden could have done this. England could have done this. Spain could have done this. Mongolia listened to the experts, acted quickly, and kept their people safe. Much of the rest of the world, especially the western world — the so-called first-world countries — failed to act quickly enough and hundreds of thousands of people have needlessly died and countless others have been left with chronic health issues, grief, and economic chaos.
As summer ramps up in North America, people are looking to get out to enjoy the weather while also trying to keep safe from Covid-19 infection. Here in Vermont, I am very much looking forward to swim hole season and have been wondering if swimming is a safe activity during the pandemic. The Atlantic’s Olga Khazan wrote about the difficulty of opening pools back up this summer:
The coronavirus can’t remain infectious in pool water, multiple experts assured me, but people who come to pools do not stay in the water the entire time. They get out, sit under the sun, and, if they’re like my neighbors, form a circle and drink a few illicit White Claws. Social-distancing guidelines are quickly forgotten.
“If someone is swimming laps, that would be pretty safe as long as they’re not spitting water everywhere,” says Angela Rasmussen, a virologist at Columbia University. “But a Las Vegas-type pool party, that would be less safe, because people are just hanging out and breathing on each other.”
This story by Christopher Reynolds in the LA Times focuses more on transmission via water (pool water, salt water, river/lake water).
“There is no data that somebody got infected this way [with coronavirus],” said professor Karin B. Michels, chair of UCLA’s Department of Epidemiology, in a recent interview.
“I can’t say it’s absolutely 100% zero risk, but I can tell you that it would never cross my mind to get COVID-19 from a swimming pool or the ocean,” said Paula Cannon, a professor of molecular microbiology and immunology at USC’s Keck School of Medicine. “It’s just extraordinarily unlikely that this would happen.”
As long as you keep your distance of course:
Rather than worry about coronavirus in water, UCLA’s Michels and USC’s Cannon said, swimmers should stay well separated and take care before and after entering the pool, lake, river or sea.
“I would be more concerned about touching the same lockers or surfaces in the changing room or on the benches outside the pool. Those are higher risk than the water itself,” Michels said. “The other thing is you have to maintain distance. … More distance is always better.”
Sorta related but not really: ten meters is definitely more distance.
After 2+ months of lockdown in most areas, a small minority of Americans want our country to go back to “normal” despite evidence and expert advice to the contrary. They want to get haircuts, not wear masks in public, go to crowded beaches, and generally go about their lives. These folks couch their desires in terms of freedom & liberty: the government has no right to infringe on the individual freedoms of its citizens.
But governments routinely do just that for all kinds of good reasons — e.g. you can’t murder someone just because you feel like it — and as Johns Hopkins’ public health historian Graham Mooney points out, there’s a precedent for a different way of thinking about freedom in the context of public health.
In response to these vehement appeals to individual freedom, public-health leaders in London, Liverpool, Manchester and elsewhere developed a powerful counterargument. They too framed their argument in terms of freedom — freedom from disease. To protect citizens’ right to be free from disease, in their view, governments and officials needed the authority to isolate those who were sick, vaccinate people, and take other steps to reduce the risk of infectious disease.
One of the most important reformers was George Buchanan, the chief medical officer for England from 1879 to 1892. He argued that cities and towns had the authority to take necessary steps to ensure the communal “sanitary welfare.” He and other reformers based their arguments on an idea developed by the 19th-century English philosopher John Stuart Mill, who is, ironically, remembered largely as a staunch defender of individual liberty. Mill articulated what he called the “harm principle,” which asserts that while individual liberty is sacrosanct, it should be limited when it will harm others: “The sole end for which mankind are warranted, individually or collectively, in interfering with the liberty and action of any of their number, is self-protection,” Mill wrote in On Liberty in 1859. Public-health reformers argued that the harm principle gave them the authority to pursue their aims.
An essay published in The Lancet in 1883 sums up this view nicely: “We cannot see that there is any undue violation of personal liberty in the sanitary authority acting for the whole community, requiring to be informed of the existence of diseases dangerous to others. A man’s liberty is not to involve risk to others,” the author wrote. “A man with smallpox has the natural liberty to travel in a cab or an omnibus; but society has a right that overrides his natural liberty, and says he shall not.”
As some places in the United States and other countries are opening back up (some very prematurely), immunologist and biologist Dr. Erin Bromage has written a practical guide to the known Covid-19 risks and how to avoid them that’s based on recent scientific research. He begins:
It seems many people are breathing some relief, and I’m not sure why. An epidemic curve has a relatively predictable upslope and once the peak is reached, the back slope can also be predicted. We have robust data from the outbreaks in China and Italy, that shows the backside of the mortality curve declines slowly, with deaths persisting for months. Assuming we have just crested in deaths at 70k, it is possible that we lose another 70,000 people over the next 6 weeks as we come off that peak. That’s what’s going to happen with a lockdown.
As states reopen, and we give the virus more fuel, all bets are off. I understand the reasons for reopening the economy, but I’ve said before, if you don’t solve the biology, the economy won’t recover.
But since things are opening up anyway (whether epidemiologists like it or not), Bromage goes through a number of scenarios you might potentially find yourself in over the next few months and what the associated risks might be. His guiding principle is that infection is caused by exposure to the virus over time — increase the time or the exposure and your risk goes up. For example, public bathrooms might give you a ton of exposure to the virus over a relatively short period of time:
Bathrooms have a lot of high touch surfaces, door handles, faucets, stall doors. So fomite transfer risk in this environment can be high. We still do not know whether a person releases infectious material in feces or just fragmented virus, but we do know that toilet flushing does aerosolize many droplets. Treat public bathrooms with extra caution (surface and air), until we know more about the risk.
But being in the same room with another person simply breathing may not carry a large risk if you limit the time.
A single breath releases 50-5000 droplets. Most of these droplets are low velocity and fall to the ground quickly. There are even fewer droplets released through nose-breathing. Importantly, due to the lack of exhalation force with a breath, viral particles from the lower respiratory areas are not expelled.
But that time would drop sharply if the person is speaking:
Speaking increases the release of respiratory droplets about 10 fold; ~200 copies of virus per minute. Again, assuming every virus is inhaled, it would take ~5 minutes of speaking face-to-face to receive the required dose.
Again, this is all indoors. Being in enclosed spaces with other humans, particularly if they are poorly ventilated, is going to hold higher risks for the foreseeable future.
The reason to highlight these different outbreaks is to show you the commonality of outbreaks of COVID-19. All these infection events were indoors, with people closely-spaced, with lots of talking, singing, or yelling. The main sources for infection are home, workplace, public transport, social gatherings, and restaurants. This accounts for 90% of all transmission events. In contrast, outbreaks spread from shopping appear to be responsible for a small percentage of traced infections. (Ref)
Importantly, of the countries performing contact tracing properly, only a single outbreak has been reported from an outdoor environment (less than 0.3% of traced infections). (ref)
The Michael Pollan version of advice for socializing during the pandemic might be: Spend time with people, not too much, mostly masked and outdoors.
As someone who suspects I may have had a mild case of Covid-19 a couple of months ago, I’ve been thinking about getting tested for antibodies. But as this video from ProPublica shows, even really accurate tests may not actually tell you all that much.
And the thing is, the “do I have Covid-19 right now” tests are plagued by the same issue.
For patients getting tested, the main concern is how to interpret the outcome: If I test negative with an RT-PCR genetic test, what are the chances I actually have the virus? Or if I test positive with an antibody test, does it actually mean I have the antibodies?
It turns out that the answers to these questions don’t just hinge on the accuracy of the test. “Mathematically, the way that works out, that actually depends on how many people in your area have Covid,” Eleanor Murray, an assistant professor of epidemiology at the Boston University School of Public Health, said.
The rarer the disease in the population, the less you’ll learn by testing.
Let’s say we have a hypothetical Covid-19 test for antibodies that is both 99 percent sensitive — meaning almost all people with antibodies will test positive — and 99 percent specific, meaning almost all people who were never infected will yield a negative result.
If you test a group of 100 uninfected people, odds are one of them will still test positive even though they don’t have the virus. Conversely, if you test 100 people who were infected, it’s likely one of them will still test negative.
Now let’s presume the virus has a prevalence rate of 1 percent, so one person in 100 carries antibodies to it. If you test 100 random people and get a positive result, what is the chance that this person was truly infected?
Deborah Birx, the White House Covid-19 response coordinator, explained the answer at a press conference on April 20: “So if you have 1 percent of your population infected and you have a test that’s only 99 percent specific, that means that when you find a positive, 50 percent of the time will be a real positive and 50 percent of the time it won’t be.”
So even if I test positive for antibodies and I assume that confers immunity, given that the number of confirmed infections in Vermont is so low (~900 statewide), it doesn’t seem like I would be justified in changing my behavior at all. I would still have to act as though I’ve never had the virus, both for my own health and the health of those around me. Maybe if I had two or three corroborating tests could I be more certain…
From Nature’s David Cyranoski, a piece that takes a look at what the latest research says about SARS-CoV-2, where it came from, and how it is able to infect the human body. I’m going to highlight a few things from the article I thought were particularly interesting. As Cyranoski has done throughout, I’d like to stress that because this virus is so new to us and the situation is moving so quickly, many of these results are based on preliminary research, have been published in pre-print papers, and haven’t been peer-reviewed.
The first is about the detective work being done to trace where SARS-CoV-2 came from and how long it’s been in existence (possibly decades).
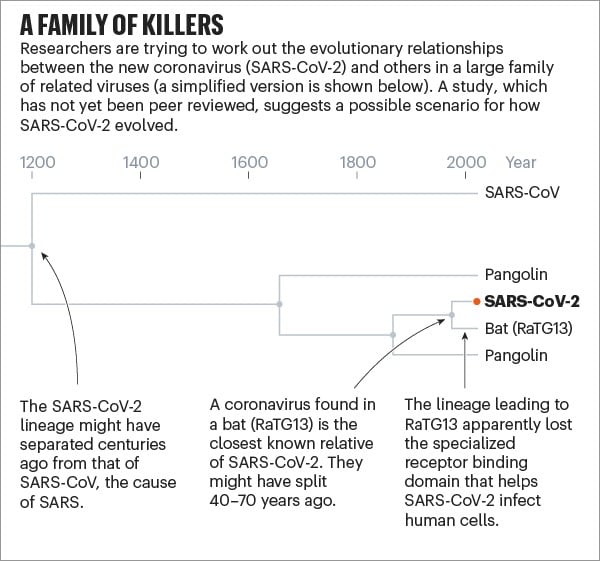
But studies released over the past few months, which have yet to be peer-reviewed, suggest that SARS-CoV-2 — or a very similar ancestor — has been hiding in some animal for decades. According to a paper posted online in March, the coronavirus lineage leading to SARS-CoV-2 split more than 140 years ago from the closely related one seen today in pangolins. Then, sometime in the past 40-70 years, the ancestors of SARS-CoV-2 separated from the bat version, which subsequently lost the effective receptor binding domain that was present in its ancestors (and remains in SARS-CoV-2). A study published on 21 April came up with very similar findings using a different dating method.
The section on how the virus acts in the body is particularly interesting because it attempts to explain the unusual and varying behaviors SARS-CoV-2 exhibits and causes in different parts of the human body. For example, SARS-CoV-2, unusually, can initially infect two places in the body: the throat and lungs.
Having these two infection points means that SARS-CoV-2 can mix the transmissibility of the common cold coronaviruses with the lethality of MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV. “It is an unfortunate and dangerous combination of this coronavirus strain,” he says.
The virus’s ability to infect and actively reproduce in the upper respiratory tract was something of a surprise, given that its close genetic relative, SARS-CoV, lacks that ability. Last month, Wendtner published results of experiments in which his team was able to culture virus from the throats of nine people with COVID-19, showing that the virus is actively reproducing and infectious there. That explains a crucial difference between the close relatives. SARS-CoV-2 can shed viral particles from the throat into saliva even before symptoms start, and these can then pass easily from person to person. SARS-CoV was much less effective at making that jump, passing only when symptoms were full-blown, making it easier to contain.
These differences have led to some confusion about the lethality of SARS-CoV-2. Some experts and media reports describe it as less deadly than SARS-CoV because it kills about 1% of the people it infects, whereas SARS-CoV killed at roughly ten times that rate. But Perlman says that’s the wrong way to look at it. SARS-CoV-2 is much better at infecting people, but many of the infections don’t progress to the lungs. “Once it gets down in the lungs, it’s probably just as deadly,” he says.
And this is a somewhat hopeful speculation on one of the many possible ways the Covid-19 pandemic could go:
“By far the most likely scenario is that the virus will continue to spread and infect most of the world population in a relatively short period of time,” says Stöhr, meaning one to two years. “Afterwards, the virus will continue to spread in the human population, likely forever.” Like the four generally mild human coronaviruses, SARS-CoV-2 would then circulate constantly and cause mainly mild upper respiratory tract infections, says Stöhr. For that reason, he adds, vaccines won’t be necessary.
Some previous studies support this argument. One showed that when people were inoculated with the common-cold coronavirus 229E, their antibody levels peaked two weeks later and were only slightly raised after a year. That did not prevent infections a year later, but subsequent infections led to few, if any, symptoms and a shorter period of viral shedding.
The OC43 coronavirus offers a model for where this pandemic might go. That virus also gives humans common colds, but genetic research from the University of Leuven in Belgium suggests that OC43 might have been a killer in the past.
But then, from a few paragraphs down:
People like to think that “the other coronaviruses were terrible and became mild”, says Perlman. “That’s an optimistic way to think about what’s going on now, but we don’t have evidence.”
For now, it’s just another thing we don’t know about this virus we learned about only 5 months ago. It’s a long road ahead, but I’m thankful that so many scientists are bent on making sense of it all.
This too-short profile of Pulitzer Prize-winning journalist Laurie Garrett, who has been writing about epidemics since the 90s, is closer to my personal feelings as to how the pandemic plays out in the US than almost anything else I’ve read.
But she can’t envision that vaccine anytime in the next year, while Covid-19 will remain a crisis much longer than that.
“I’ve been telling everybody that my event horizon is about 36 months, and that’s my best-case scenario,” she said.
“I’m quite certain that this is going to go in waves,” she added. “It won’t be a tsunami that comes across America all at once and then retreats all at once. It will be micro-waves that shoot up in Des Moines and then in New Orleans and then in Houston and so on, and it’s going to affect how people think about all kinds of things.”
They’ll re-evaluate the importance of travel. They’ll reassess their use of mass transit. They’ll revisit the need for face-to-face business meetings. They’ll reappraise having their kids go to college out of state.
Much of the federal government’s response has been to help big business, and the wealthy are going to have opportunities to not only ride out the storm more easily but to take advantage:
If America enters the next wave of coronavirus infections “with the wealthy having gotten somehow wealthier off this pandemic by hedging, by shorting, by doing all the nasty things that they do, and we come out of our rabbit holes and realize, ‘Oh, my God, it’s not just that everyone I love is unemployed or underemployed and can’t make their maintenance or their mortgage payments or their rent payments, but now all of a sudden those jerks that were flying around in private helicopters are now flying on private personal jets and they own an island that they go to and they don’t care whether or not our streets are safe,’ then I think we could have massive political disruption.”
I could quote something from just about every paragraph, but for now I’ll just do one more excerpt and you can go and read the rest.
Garrett recounted her time at Harvard. “The medical school is all marble, with these grand columns,” she said. “The school of public health is this funky building, the ugliest possible architecture, with the ceilings falling in.”
“That’s America?” I asked.
“That’s America,” she said.
See also Dave Eggers’ pandemic Q&A, which shares a certain pessimistic honesty with Garrett’s thoughts.
Creative technologist Nicky Case and epidemiologist Marcel Salathé have teamed up to produce a concise but thorough playable explainer about important epidemiological concepts, how we could/should respond to the Covid-19 pandemic, and different scenarios about what the next few years could look like.
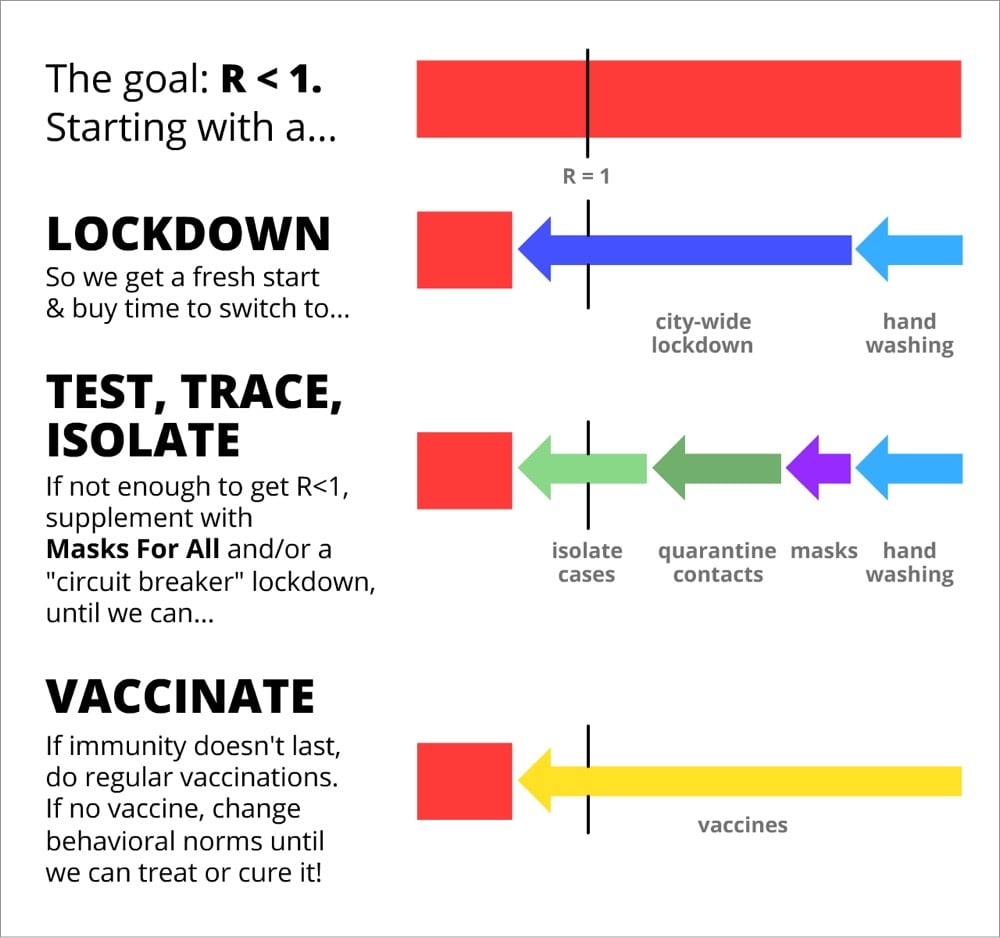
If you’ve been keeping up with the various models and experts’ plans (test/trace/isolate, etc.), there’s not a lot new here until close to end, but it is pretty comprehensive and the playable simulations are really useful. The whole thing takes about 30 minutes to get through, but at the end, you will have an excellent simplified understanding of what this virus could do to us and what we can do to mitigate its effects.
Isolating symptomatic cases would reduce R by up to 40%, and quarantining their pre/a-symptomatic contacts would reduce R by up to 50%:
Thus, even without 100% contact quarantining, we can get R < 1 without a lockdown! Much better for our mental & financial health. (As for the cost to folks who have to self-isolate/quarantine, governments should support them — pay for the tests, job protection, subsidized paid leave, etc. Still way cheaper than intermittent lockdown.)
The problem with this explainer, as excellent as it is, is the problem with all of these plans: many government officials on both the state & federal level don’t seem interested in listening to the experts. It is also unclear — if the unmasked crowds gathering in American cities during this past weekend’s warm weather are any indication — that Americans will be willing to take the steps necessary to keep each other safe. I’m not sure what it’s going to take to address those situations, but I don’t think playable graphs are going to help that much.
As Ed Yong notes in his helpful overview of the pandemic, this is such a huge and quickly moving event that it’s difficult to know what’s happening. Lately, I’ve been seeking information on Covid-19’s presenting symptoms after seeing a bunch of anecdotal data from various sources.
In the early days of the epidemic (January, February, and into March), people were told by the CDC and other public health officials to watch out for three specific symptoms: fever, a dry cough, and shortness of breath. In many areas, testing was restricted to people who exhibited only those symptoms. Slowly, as more data is gathered, the profile of the presenting symptoms has started to shift. From a New York magazine piece by David Wallace-Wells on Monday:
While the CDC does list fever as the top symptom of COVID-19, so confidently that for weeks patients were turned away from testing sites if they didn’t have an elevated temperature, according to the Journal of the American Medical Association, as many as 70 percent of patients sick enough to be admitted to New York State’s largest hospital system did not have a fever.
Over the past few months, Boston’s Brigham and Women’s Hospital has been compiling and revising, in real time, treatment guidelines for COVID-19 which have become a trusted clearinghouse of best-practices information for doctors throughout the country. According to those guidelines, as few as 44 percent of coronavirus patients presented with a fever (though, in their meta-analysis, the uncertainty is quite high, with a range of 44 to 94 percent). Cough is more common, according to Brigham and Women’s, with between 68 percent and 83 percent of patients presenting with some cough — though that means as many as three in ten sick enough to be hospitalized won’t be coughing. As for shortness of breath, the Brigham and Women’s estimate runs as low as 11 percent. The high end is only 40 percent, which would still mean that more patients hospitalized for COVID-19 do not have shortness of breath than do. At the low end of that range, shortness of breath would be roughly as common among COVID-19 patients as confusion (9 percent), headache (8 to 14 percent), and nausea and diarrhea (3 to 17 percent).
Recently, as noted by the Washington Post, the CDC has changed their list of Covid-19 symptoms to watch out for. They now list two main symptoms (cough & shortness of breath) and several additional symptoms (fever, chills, repeated shaking with chills, muscle pain, headache, sore throat, new loss of taste or smell). They also note that “this list is not all inclusive”. Compare that with their list from mid-February.
In addition, there’s evidence that children might have different symptoms (including stomach issues or diarrhea), doctors are reporting seeing “COVID toes” on some patients, and you might want to look at earlier data from these three studies about symptoms observed in Wuhan and greater China.
The reason I’m interested in this shift in presenting symptoms is that on the last day or two of my trip to Asia, I got sick — and I’ve been wondering if it was Covid-19.
Here’s the timeline: starting on Jan 21, I was in Saigon, Vietnam for two weeks, then in Singapore for 4 days, and then Doha, Qatar for 48 hours. The day I landed in Doha, Feb 9, I started to feel a little off, and definitely felt sick the next day. I had a sore throat, headache, and congestion (stuffy nose) for the first few days. There was also some fatigue/tiredness but I was jetlagged too so… All the symptoms were mild and it felt like a normal cold to me. Here’s how I wrote about it in my travelogue:
I got sick on the last day of the trip, which turned into a full-blown cold when I got home. I dutifully wore my mask on the plane and in telling friends & family about how I was feeling, I felt obliged to text “***NOT*** coronavirus, completely different symptoms!!”
I flew back to the US on Feb 11 (I wore a mask the entire time in the Doha airport, on the plane, and even in the Boston airport, which no one else was doing). I lost my sense of taste and smell for about 2 days, which was a little unnerving but has happened to me with past colds. At no point did I have even the tiniest bit of fever or shortness of breath. The illness did drag on though — I felt run-down for a few weeks and a very slight cough that developed about a week and a half after I got sick lingered for weeks.
According to guidance from the WHO, CDC, and public health officials at the time, none of my initial symptoms were a match for Covid-19. I thought about getting a test or going to the doctor, but in the US in mid-February, and especially in Vermont, there were no tests available for someone with a mild cold and no fever. But looking at the CDC’s current list of symptoms — which include headache, sore throat, and new loss of taste or smell — and considering that I’d been in Vietnam and Singapore when cases were reported in both places, it seems plausible to me that my illness could have been a mild case of Covid-19. Hopefully it wasn’t, but I’ll be getting an antibody test once they are (hopefully) more widely available, even though the results won’t be super reliable.
Update: More on the changing profile of Covid-19 symptoms from a sample size of more than 30,000 tests.
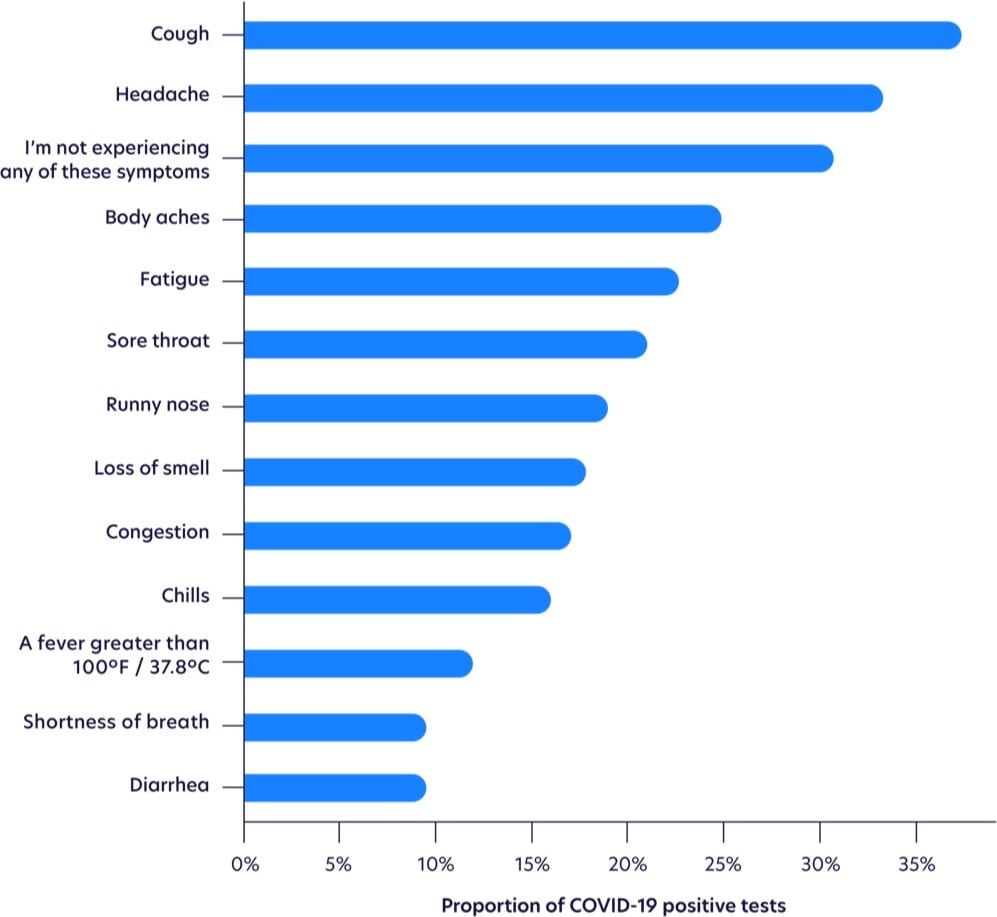
Fever is waaay down on the list.
While not as common as other symptoms, loss of smell was the most highly correlated with testing positive, as shown with odds ratios below, after adjusting for age and gender. Those with loss of smell were more likely to test positive for COVID-19 than those with a high fever.
Seeing this makes me think more than ever that I had it. I had three of the top five symptoms, plus an eventual cough (the most common symptom) and a loss of smell & taste (the most highly correlated symptom). The timing of the onset of my symptoms (my first day in Qatar) indicates that I probably got infected on my last day in Vietnam, in transit from Vietnam to Singapore (1 2-hr plane ride, 2 airports, 1 taxi, 1 train ride), or on my first day in Singapore. But I went to so many busy places during that time that it’s impossible to know where I might have gotten infected (or who I then went on to unwittingly infect).
Update: A few weeks ago, I noticed some horizontal lines on several of my toenails, a phenomenon I’d never seen before. When I finally googled it, I discovered they’re called Beau’s lines and they can show up when the body has been stressed by illness or disease. Hmm. From the Wikipedia page:
Some other reasons for these lines include trauma, coronary occlusion, hypocalcaemia, and skin disease. They may be a sign of systemic disease, or may also be caused by an illness of the body, as well as drugs used in chemotherapy, or malnutrition. Beau’s lines can also be seen one to two months after the onset of fever in children with Kawasaki disease.
From the Mayo Clinic:
Conditions associated with Beau’s lines include uncontrolled diabetes and peripheral vascular disease, as well as illnesses associated with a high fever, such as scarlet fever, measles, mumps and pneumonia.
From the estimated growth of my nails, it seems as though whatever disruption that caused the Beau’s lines happened 5-6 months ago, which lines up with my early February illness that I believe was Covid-19. Covid-19 can definitely affect the vascular systems of infected persons. Kawasaki disease is a vascular disease and a similar syndrome in children resulting from SARS-CoV-2 exposure is currently under investigation. And here’s a paper from December 1971 that tracked the development of Beau’s lines in several people who were ill during the 1968 flu pandemic (an H3N2 strain of the influenza A virus) — coronaviruses and influenza viruses are different but this is still an indicator that viruses can result in Beau’s lines. “Covid toe” has been observed in many Covid-19 patients. Harvard dermatologist and epidemiologist Dr. Esther Freeman reports that people may be experiencing hair loss due to Covid-19.
I couldn’t find any scientific literature about the possible correlation of Covid-19 and Beau’s lines, but I did find some suggestive anecdotal information. I found several people on Twitter who noticed lines in their nails (both fingers and toes) and who also have confirmed or suspected cases of Covid-19. And if you go to Google’s search bar and type “Beau’s lines c”, 3 of the 10 autocomplete suggestions are related to Covid-19, which indicates that people are searching for it (but not enough to register on Google Trends).
But I am definitely intrigued. Are dermatologists and podiatrists seeing Beau’s lines on patients who have previously tested positive for Covid-19? Have people who have tested positive noticed them? Email me at [email protected] if you have any info about this; I’d love to get to the bottom of this.
In early March, Dr. Caroline Schulman was responsible for calling patients at her hospital to tell them they had tested positive for Covid-19. She shared some of her experiences in a piece for Stat.
Erik lives with his entire family in a one-room rental house with eight other occupants. He didn’t understand the precautions for preventing the spread of Covid-19 and had regularly been socializing in the apartment. He kept asking how to file for unemployment and how to isolate the household when the house itself could barely hold those living in it.
Jeff lives alone. He has a chronic blood condition and is struggling to get by. A few hours before we talked, he had resumed his job as a ride share driver because he needed to make ends meet.
Angela is 40 years old and has one of the preexisting conditions that put people at high risk for serious complications of Covid-19. When we spoke, she told me that she was feeling better, but that her home life was difficult. Her children had returned home after Mayor Muriel Bowser issued a stay-at-home order for the District of Columbia. She asked her kids to take precautions, but they continued to leave the house often. One son brought home his girlfriend, who had a cough, and displaced Angela from her room. She was unable to make an appointment with her primary doctor and couldn’t afford her medical supplies because of insurance issues. When I spoke with her, she sounded well and had no classic symptoms, but something didn’t sound right. I arranged a televisit that afternoon to have her evaluated more closely. By the time she got the call two hours later, she was so short of breath she could barely speak. When an ambulance arrived to take her to the hospital, her oxygen levels were dangerously low.
Reading through these stories, I just kept thinking about the measures that are going to be necessary if we’re going to safely restart public life in America — hygiene, mask wearing, some social distancing, and eventually a vaccine — and how our collective safety is going to depend on individuals doing the right thing. And most people will. But it’s clear that, especially without coherent national leadership & economic support, some people will be unable to take the necessary precautions for economic reasons and others won’t because they don’t understand why these measures are necessary, don’t trust science, or a dozen other reasons.
Working under the direction of The Edmond J. Safra Center for Ethics at Harvard University, a bipartisan group of experts in public health, economics, technology, and ethics have produced a plan for a phased reopening of public life in the United States through testing, tracing, and supported isolation. The video above summarizes the plan and here’s the full plan in the form of a 56-page PDF.
“Roadmap to Pandemic Resilience: Massive Scale Testing, Tracing, and Supported Isolation (TTSI) as the Path to Pandemic Resilience for a Free Society,” lays out how a massive scale-up of testing, paired with contact tracing and supported isolation, can rebuild trust in our personal safety and re-mobilize the U.S. economy.
Among the report’s top recommendations is the need to deliver at least 5 million tests per day by early June to help ensure a safe social opening. This number will need to increase to 20 million tests per day by mid-summer to fully re-mobilize the economy.
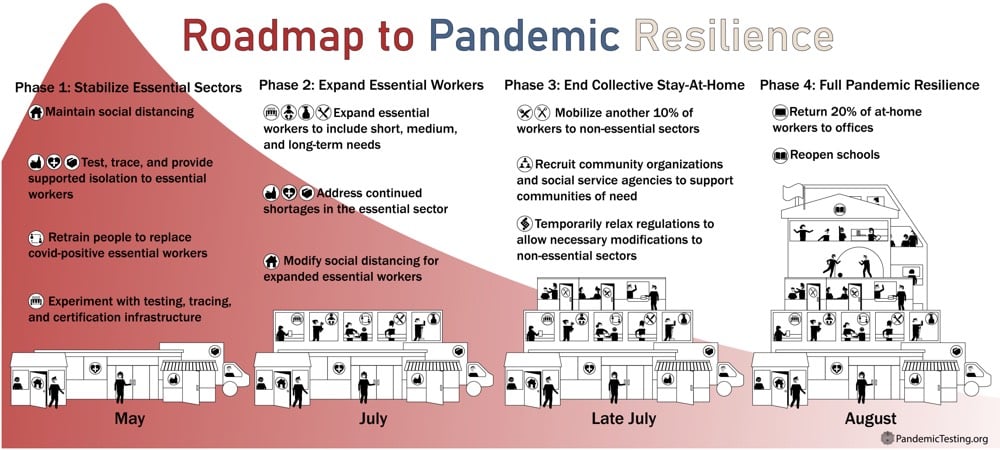
From the paper, here’s a quick overview:
What we need to do is much bigger than most people realize. We need to massively scale-up testing, contact tracing, isolation, and quarantine-together with providing the resources to make these possible for all individuals.
Broad and rapid access to testing is vital for disease monitoring, rapid public health response, and disease control.
We need to deliver 5 million tests per day by early June to deliver a safe social reopening. This number will need to increase over time (ideally by late July) to 20 million a day to fully remobilize the economy. We acknowledge that even this number may not be high enough to protect public health. In that considerably less likely eventuality, we will need to scale-up testing much further. By the time we know if we need to do that, we should be in a better position to know how to do it. In any situation, achieving these numbers depends on testing innovation.
Between now and August, we should phase in economic mobilization in sync with growth in our capacity to provide sustainable testing programs for mobilized sectors of the workforce.
The great value of this approach is that it will prevent cycles of opening up and shutting down. It allows us to steadily reopen the parts of the economy that have been shut down, protect our frontline workers, and contain the virus to levels where it can be effectively managed and treated until we can find a vaccine.
We can have bottom-up innovation and participation and top-down direction and protection at the same time; that is what our federal system is designed for.
This policy roadmap lays out how massive testing plus contact tracing plus social isolation with strong social supports, or TTSI, can rebuild trust in our personal safety and the safety of those we love. This will in turn support a renewal of mobility and mobilization of the economy. This paper is designed to educate the American public about what is emerging as a consensus national strategy.
The plan seems consistent with what economist Paul Romer has been saying — Without More Tests, America Can’t Reopen (And to make matters worse, we’re testing the wrong people) — and with the approach Hong Kong has been taking — Test and trace: lessons from Hong Kong on avoiding a coronavirus lockdown. See also the 4 plans to end social distancing, explained.
Unfortunately for this plan and for all of us, I have a feeling that the first true step in any rational plan to reopen the United States without unnecessary death and/or massive economic disruption that lasts for years is the removal of Donald Trump from office (and possibly also the end of the Republican-controlled Senate). Barring that, the ineffectual circus continues. (via @riondotnu)
Thousands of scientific research papers on Covid-19 and SARS-CoV-2 are being published each week and with them comes a clearer picture of the virus and the disease it causes. There’s still a lot we don’t know, but this piece from Science magazine is the best synthesis of the emerging science that I have read. It details a virus that “acts like no microbe humanity has ever seen” and affects not only the lungs but also the kidneys, heart, brain, and the intestines.
As the number of confirmed cases of COVID-19 surges past 2.2 million globally and deaths surpass 150,000, clinicians and pathologists are struggling to understand the damage wrought by the coronavirus as it tears through the body. They are realizing that although the lungs are ground zero, its reach can extend to many organs including the heart and blood vessels, kidneys, gut, and brain.
“[The disease] can attack almost anything in the body with devastating consequences,” says cardiologist Harlan Krumholz of Yale University and Yale-New Haven Hospital, who is leading multiple efforts to gather clinical data on COVID-19. “Its ferocity is breathtaking and humbling.”
Understanding the rampage could help the doctors on the front lines treat the fraction of infected people who become desperately and sometimes mysteriously ill. Does a dangerous, newly observed tendency to blood clotting transform some mild cases into life-threatening emergencies? Is an overzealous immune response behind the worst cases, suggesting treatment with immune-suppressing drugs could help? What explains the startlingly low blood oxygen that some physicians are reporting in patients who nonetheless are not gasping for breath? “Taking a systems approach may be beneficial as we start thinking about therapies,” says Nilam Mangalmurti, a pulmonary intensivist at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania (HUP).
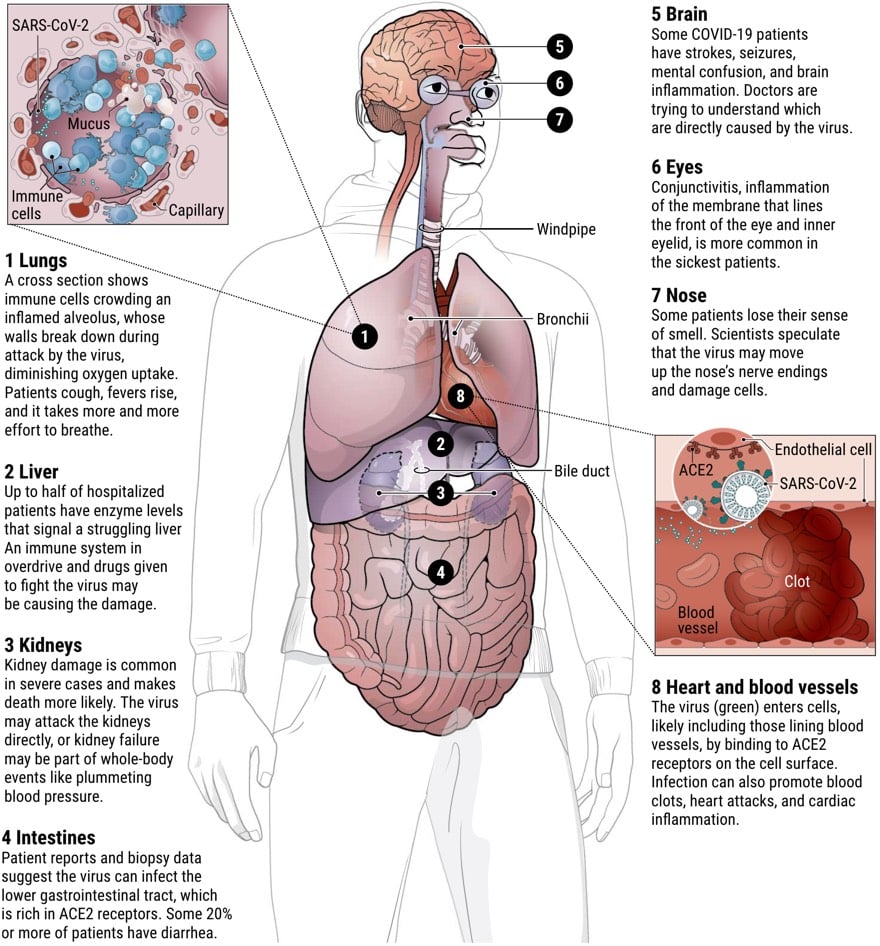
I’ve been hearing that although Covid-19’s attack begins in the lungs, it is as much a vascular disease as it is a respiratory disease — and there is some evidence emerging to support this view:
If COVID-19 targets blood vessels, that could also help explain why patients with pre-existing damage to those vessels, for example from diabetes and high blood pressure, face higher risk of serious disease. Recent Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) data on hospitalized patients in 14 U.S. states found that about one-third had chronic lung disease-but nearly as many had diabetes, and fully half had pre-existing high blood pressure.
Mangalmurti says she has been “shocked by the fact that we don’t have a huge number of asthmatics” or patients with other respiratory diseases in HUP’s ICU. “It’s very striking to us that risk factors seem to be vascular: diabetes, obesity, age, hypertension.”
What struck me most about this piece is the sheer energy of the vast network of minds bent towards understanding this thing with the hope of beating it as soon as possible. This is the scientific method at work right here, in all its urgent & messy glory.
From Retro Report, a short video about how epidemics, past and present, have been represented in music. Blues musicians sang about the 1918 flu pandemic and pop stars wrote songs about HIV/AIDS.
A disease that killed tens of millions of people, more than the number who died in World War I, might not seem like a promising subject for a song, but the legendary Texas bluesman Blind Willie Johnson didn’t see it that way. In Dallas in 1928, Johnson recorded “Jesus Is Coming Soon,” an intense chronicle of the ravaging influenza pandemic of 1918-1919. In a growl that conveyed the horror of the illness, as well as its scarifying ubiquity, Johnson declared that the “great disease was mighty and the people were sick everywhere / It was an epidemic, it floated through the air.”
Other lines seem as if they could have been written yesterday: “Well, the nobles said to the people, ‘You better close your public schools / Until the events of death has ended, you better close your churches, too.’”
Newer posts
Older posts














Socials & More