Is liberal democracy in trouble? “Warning signs are flashing red.”
Political scientists Yascha Mounk and Roberto Stefan Foa have been doing research on the stability of contemporary liberal democracies, looking in particular at the assumption a country becomes a democracy, it will stay that way. Their conclusion? We may be in trouble: “liberal democracies around the world may be at serious risk of decline”.
But since 2005, Freedom House’s index has shown a decline in global freedom each year. Is that a statistical anomaly, a result of a few random events in a relatively short period of time? Or does it indicate a meaningful pattern?
Mr. Mounk and Mr. Foa developed a three-factor formula to answer that question. Mr. Mounk thinks of it as an early-warning system, and it works something like a medical test: a way to detect that a democracy is ill before it develops full-blown symptoms.
The first factor was public support: How important do citizens think it is for their country to remain democratic? The second was public openness to nondemocratic forms of government, such as military rule. And the third factor was whether “antisystem parties and movements” — political parties and other major players whose core message is that the current system is illegitimate — were gaining support.
Regarding that first factor, public support for democracy, their research indicates a worrying trend: younger people around the world think it’s less “essential” to live in a democracy.
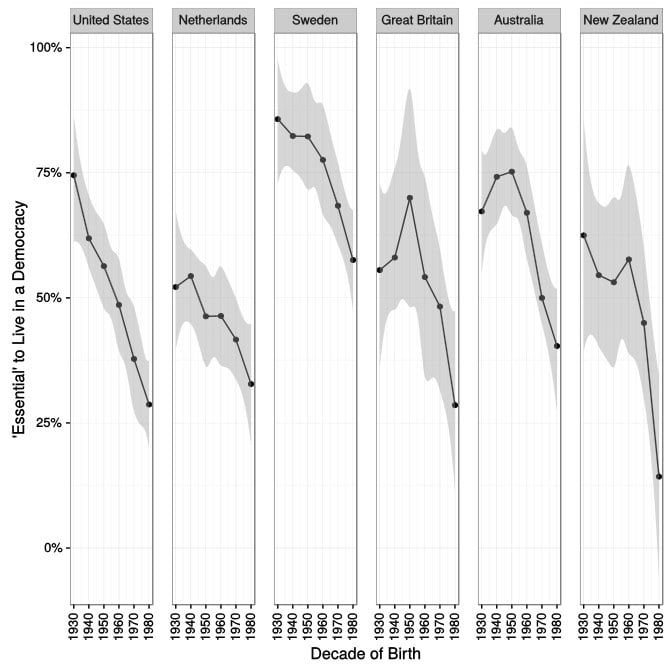
Younger people would also be more in favor of military rule:
Support for autocratic alternatives is rising, too. Drawing on data from the European and World Values Surveys, the researchers found that the share of Americans who say that army rule would be a “good” or “very good” thing had risen to 1 in 6 in 2014, compared with 1 in 16 in 1995.
That trend is particularly strong among young people. For instance, in a previously published paper, the researchers calculated that 43 percent of older Americans believed it was illegitimate for the military to take over if the government were incompetent or failing to do its job, but only 19 percent of millennials agreed. The same generational divide showed up in Europe, where 53 percent of older people thought a military takeover would be illegitimate, while only 36 percent of millennials agreed.
What’s interesting is that Trump, who Mounk believes is a threat to liberal democracy in the US, drew his support from older Americans, which would seem to be a contradiction. It is also unclear if young people have always felt this way (i.e. do people appreciate democracy more as they get older?) or if this is a newly growing sentiment (i.e. people are now less appreciative of democracy, young people particularly so).
Something I think about often is cultural memory and how it shifts, seen most notably on kottke.org in my mild obsession with The Great Span. Back in July, writer John Scalzi tweeted:
Sometimes feels like a strong correlation between WWII passing from living memory, and autocracy seemingly getting more popular.
Scalzi is on to something here, I think. Those who fought in or lived through World War II are either dead or dying. Their children, the Baby Boomers, had a very different experience in hunky dory Leave It to Beaver postwar America.1 Anyone under 50 probably doesn’t remember anything significant about the Vietnam War and anyone under 35 didn’t really experience the Cold War.2 Couple that with an increasingly poor educational experience in many areas of the country and it seems as though Americans have forgotten how bad it was (Stalin, Hitler, the Holocaust, Vietnam, the Cold War) and take for granted the rights and protections that liberal democracy, despite its faults, offers its citizens. Shame on us if we throw all of that hard-fought progress away in exchange for — how did Franklin put it? — “a little temporary safety”.
Update: The graph above showing public support for democracy is misleading and overly dramatic. Looking at the average scores is more instructive for people’s feelings on democracy:
So where does this graph go wrong? It plots the percentage of people who answer 10, and it treats everyone else the same. The graph treats the people who place themselves at 1 as having the same commitment to democracy as those who answer 9. In reality, almost no one (less than 1 percent) said that democracy is “not at all important.”
Here’s a less misleading graph:
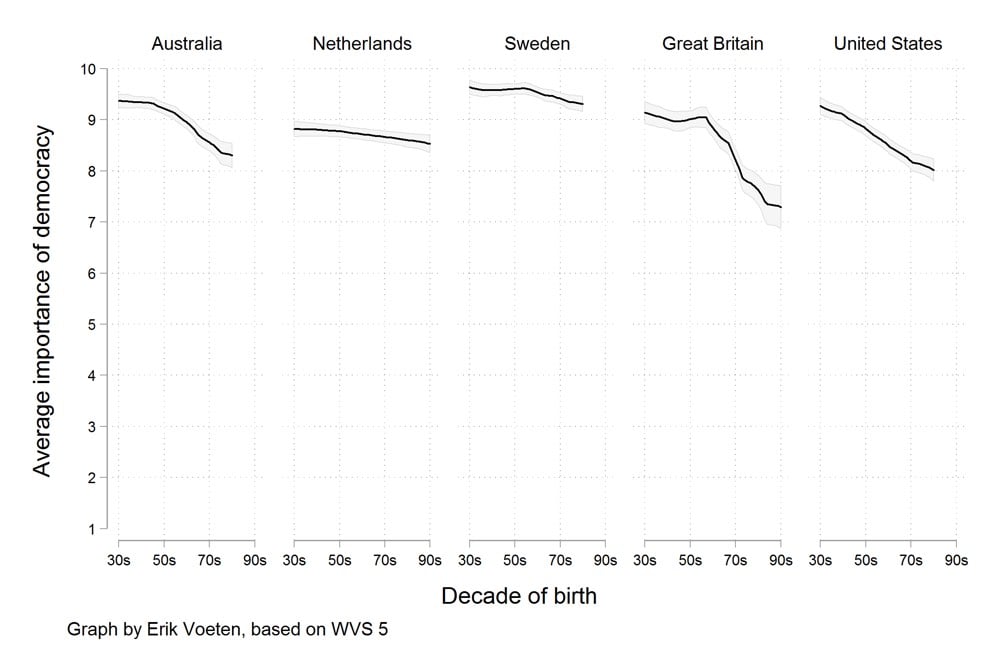
The kicker?
Vast majorities of younger people in the West still attach great importance to living in a democracy.
Well, white male Baby Boomers did. Everyone else, less so.↩
I remember the Cold War vividly — it’s why an increasingly autocratic Putin-led Russia scares the shit out of me — that feeling of ominous dread, day after day, that the world could end, actually end. I’ve only felt that way one other time in my life: in the months after 9/11. And that feeling passed after many months…the Cold War dread was constant for years.↩




Socials & More