kottke.org posts about marathons
There was a race in Paris where waiters from all the restaurants and cafes and hotels rush through the streets carrying trays with water, croissants, and empty cups of coffee. The race started around 1914, but then it stopped for the last 13 years and now they’re doing it again because of the Olympics next this year. The runners can switch hands, but they can’t carry the tray with two hands, and if their glass has less than 10cm of water when they finish, they get 30 seconds added to their finish time. Congratulations to this year’s winners, Pauline Van Wymeersch and Samy Lamrous. At the end of the race the guy said, “You’re finished!” And the winners said, “No, we’re French.”

In case anyone saw the news that Lil Nas X ran a half-marathon last weekend and then thought, Hm I wonder if other celebrities have run marathons? (as I did), the answer is: Yes, a lot, and last fall Runners World put together a long list of them, with each of the runners’ times. Shoutout to Bryan Cranston for running a 3:20! 🔥
Elsewhere in marathon news, Romper has a good story about a marathoner recovering from a birth injury. (“I’m losing my mind a little bit.”)
Over the course of 24 hours, Beau Miles ran around his mile-long block once every hour (plus a few more at the beginning) to complete a marathon in a day. But he also did a bunch of other stuff along the way: cooked dinner, made a table, fixed things, picked up trash, played Scrabble, got a bit of sleep, and made the short film above.
A different kind of marathon; running one lap an hour, for 24hrs, around my perfectly mile long block. The rest of the time I do as much as possible; making things, odd jobs, fixing stuff. It’s about running, doing, and thinking.
This past weekend in Austria, Eliud Kipchoge ran the marathon distance of 26.2 miles in 1 hour, 59 minutes, and 40 seconds, the first person in recorded history to break the two-hour marathon barrier, a feat once thought impossible. Wanting to know a bit more about how Kipchoge did it, I watched a pair of videos. The first was from Mike Boyd (who you might have seen learning how to kickflip a skateboard in under 6 hours) and it’s very much from an interested fan’s perspective.
Wired has been following Kipchoge’s attempts at a faster marathon, particularly the technology angle, and in their video, they talk with the Mayo Clinic’s Dr. Michael Joyner, who predicted in a 1991 paper that a sub-2:00 marathon was possible.
Boyd’s video references this paper as well. From a piece that Joyner wrote about his paper:
During the 1980s, ideas emerged about how maximum oxygen consumption, lactate threshold and running economy interacted to determine distance running performance. During medical school around 1985, I started think about how a person could run if he/she had the best laboratory values ever recorded for all three variables. I came up with an estimated time a few seconds faster than 1:58!
So how did Kipchoge run so fast? Well, the answer has to do with another interesting thing about this whole thing: his effort did not set an official world record for the marathon. From The Atlantic, The Greatest, Fakest World Record:
The planning that went into the event was a fantasy of perfectionism. The organizers scouted out a six-mile circuit along the Danube River that was flat, straight, and close to sea level. Parts of the road were marked with the fastest possible route, and a car guided the runners by projecting its own disco-like laser in front of them to show the correct pace. The pacesetters, a murderers’ row of Olympians and other distance stars, ran seven-at-a-time in a wind-blocking formation devised by an expert of aerodynamics. (Imagine the Mighty Ducks’ “flying V,” but reversed.)
Kipchoge himself came equipped with an updated, still-unreleased version of Nike’s controversial Vaporfly shoes, which, research appears to confirm, lower marathoners’ times. He had unfettered access to his favorite carbohydrate-rich drink, courtesy of a cyclist who rode alongside the group. And the event’s start time was scheduled within an eight-day window to ensure the best possible weather.
In an official marathon attempt, you’re not allowed to have pacesetters rotating in and out, refreshment via bicycle, or a pace car lighting the way. They touch on this in the Wired video, but technology has been wrapped up in human athletic achievement for more than a century at least. Compared to a runner competing in 1960 — when the record was 2:15:16, set by Abebe Bikila in bare feet — runners today have the benefit of better training techniques, superior knowledge of human physiology, better shoes, corporate sponsorships & other assistance, lightweight clothes that wick away moisture and don’t chafe, specially designed diets, better in-race nutrition, and, let’s be honest here, performance-enhancing drugs.
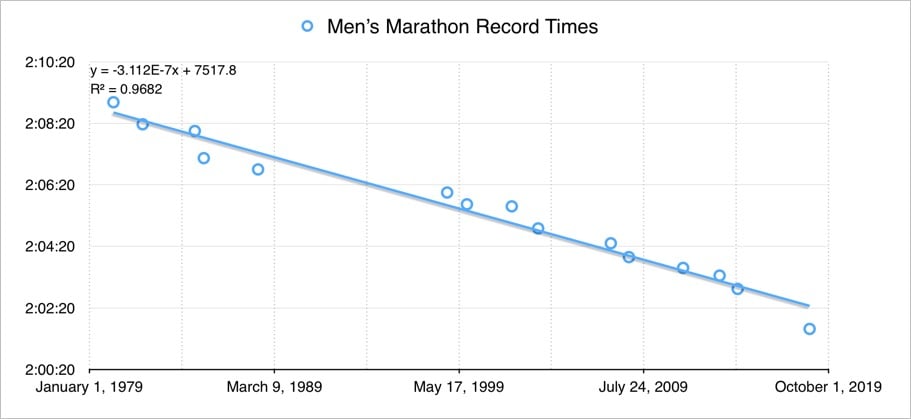
Drugs aside, all that is fine to use in an official marathon attempt, but racing alone with pacesetters (or downhill) is verboten. It’s always interesting where they draw the line on the use of technology in athletics. I think the most you can say at this point is that even with all these advantages, Kipchoge is perhaps the only person in the world right now who is capable of breaking the 2-hour barrier. But in two or three years? My guess is that 2 hours will be broken in an actual race in the next 5-7 years, even though a rough linear analysis I just did using men’s marathon record times since 1980 indicates that no one will run under 2 hours until 2033.
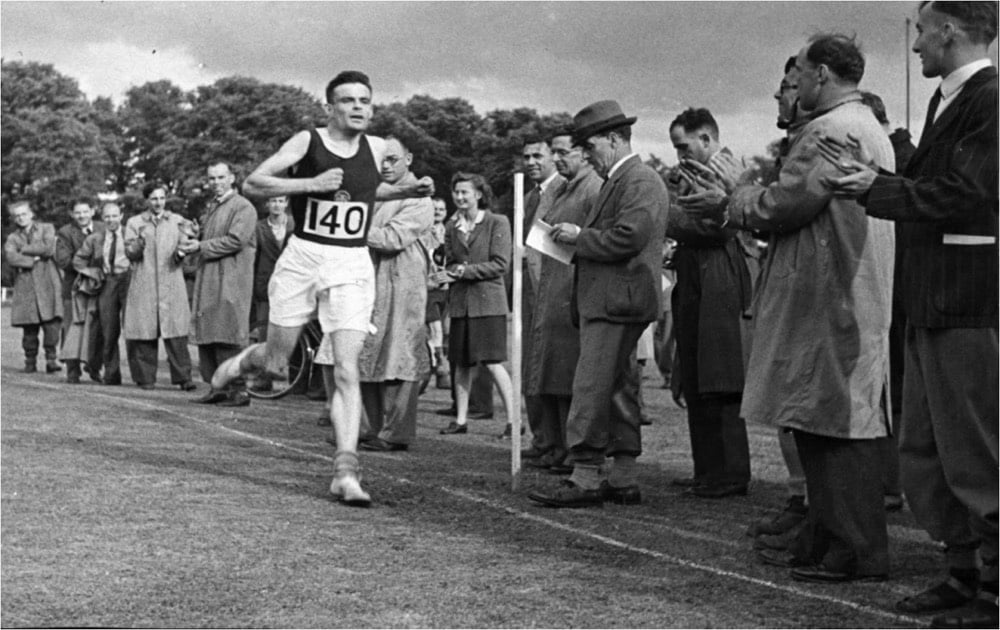

Computer scientist, mathematician, and all-around supergenius Alan Turing, who played a pivotal role in breaking secret German codes during WWII and developing the conceptual framework for the modern general purpose computer, was also a cracking good runner.
He was a runner who, like many others, came to the sport rather late. According to an article by Pat Butcher, he did not compete as an undergraduate at Cambridge, preferring to row. But after winning his fellowship to King’s College, he began running with more purpose. He is said to have often run a route from Cambridge to Ely and back, a distance of 50 kilometers.
It’s also said Turing would occasionally sometimes run to London for meetings, a distance of 40 miles. In 1947, after only two years of training, Turing ran a marathon in 2:46. He was even in contention for a spot on the British Olympic team for 1948 before an injury held him to fifth place at the trials. Had he competed and run at his personal best time, he would have finished 15th.
As the photo above shows, Turing had a brute force running style, not unlike the machine he helped design to break Enigma coded messages. He ran, he said, to relieve stress.
“We heard him rather than saw him. He made a terrible grunting noise when he was running, but before we could say anything to him, he was past us like a shot out of a gun. A couple of nights later we caught up with him long enough for me to ask who he ran for. When he said nobody, we invited him to join Walton. He did, and immediately became our best runner… I asked him one day why he punished himself so much in training. He told me ‘I have such a stressful job that the only way I can get it out of my mind is by running hard; it’s the only way I can get some release.’”
I found out about Turing’s running prowess via the Wikipedia page of non-professional marathon runners. Turing is quite high on the list, particularly if you filter out world class athletes from other sports. Also on the list, just above Turing, is Wolfgang Ketterle, a Nobel Prize-winning physicist who ran a 2:44 in Boston in 2014 at the age of 56.
The Boston Marathon was run yesterday under terribly rainy and windy conditions and many of the top competitors didn’t do so well. But as Dennis Young explains, that made room for some unusual names at the top of the winners’ list. The winner on the men’s side was Yuki Kawauchi, an amateur Japanese runner who runs in about one marathon a month (the elite pro runners only do ~2-3 a year), trains in his spare time from his government job, but has run the most sub-2:12 marathons ever.
This was at least his 71st competitive marathon since the beginning of 2012-averaging just under one a month. Overall, he’s run in at least 81 marathons.
He’s run 26 of them faster than 2:12 and 79 of them under 2:20. Both of those numbers are world records.
In January, Kawauchi ran a 2:18:59 marathon in Marshfield, Massachusetts in one-degree weather. He was the only finisher.
That race gave him the most marathons ever run under 2:20; he finished two more between then and Boston. (Obviously he was the only one of his competitors to have already run a marathon this year. Today was his fourth of 2018.)
Oh, and to prep for Boston, he ran a half-marathon in a panda suit. More on Kawauchi and his unusual training methods here. On the women’s side, Desi Linden was the first American woman to win the race in 33 years, beating the field by over four minutes, even after she hung back mid-race to help a fellow American runner re-join the pack.
She told an interviewer on the broadcast that she felt so bad early on that she figured she’d do what she could to help an American win. When Shalane Flanagan sprinted off the course for a bathroom break roughly 12 miles in, it was Linden who hung back and waited for Flanagan before helping her re-catch the pack. A little more than an hour later, Linden had the title wrapped up.
The women’s second place finisher was perhaps even more surprising. Like Kawauchi, Sarah Sellers is an amateur runner with a full-time job (she’s a nurse in Arizona), but unlike the prolific Japanese marathoner, Boston was only Sellers’ second marathon. She didn’t believe she’d gotten second, even when officials told her, which reminded me of Ester Ledecka’s Super-G victory in the 2018 Winter Olympics.
In what other highly visible and competitive sport can amateurs fare so well against professionals? Aside from the accountant who recently played goalie in an NHL game, it’s nearly unimaginable for an amateur to step into one of the major team sports and compete at a high level. Maybe golf?
In 1967, Kathrine Switzer officially entered the Boston Marathon, which was an all-male event at the time. Two miles in, race officials caught their mistake and one of them tried to remove her from the course. Switzer’s boyfriend intervened on her behalf:

She finished the race but was later disqualified. (via mlkshk)
Yes.
And then — it was mile 23 or 24 I think — my forearms started cramping. I didn’t even think I was using forearms. And then the crusty dried salt caking onto my face somehow got under my contacts. And my thighs had started chafing so I had to curl my shorts up inside themselves. So, in a few miles, I had gone from a runner, to a powerwalker, to this squinting blind torture victim.
If you’re running on a treadmill in Bismarck, North Dakota or Flagstaff Arizona or while orbiting the earth, are you really running the Boston Marathon?
For those unlucky enough not to get a slot, running in a marathon can be achieved by buying somone else’s bib or just photocopying a friend’s. Bibs for the upcoming NYC marathon are going for a few hundred dollars on eBay and Craigslist. (via clusterflock)









Socials & More