Biodegradable Food Containers Inspired by Egg Shells & Orange Peels
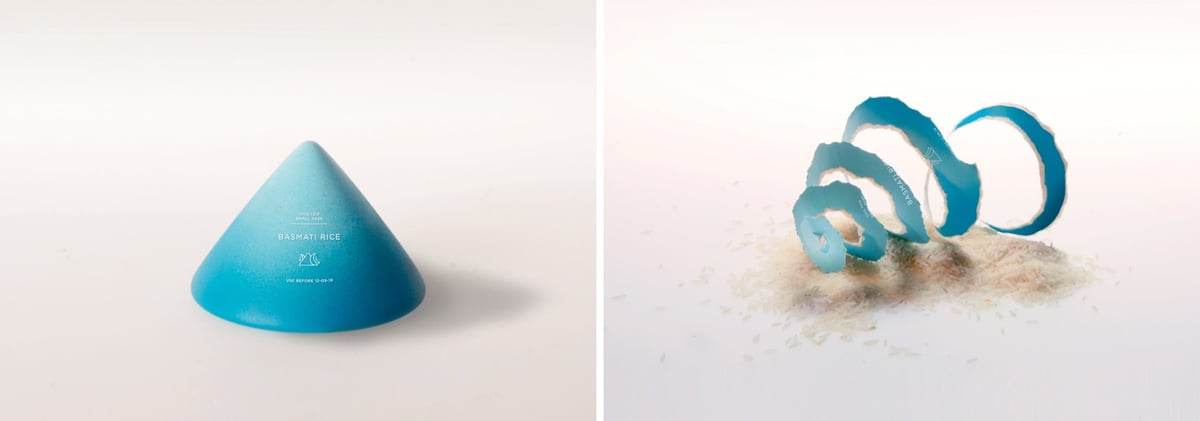


Inspired by natural packaging like egg shells and orange peels, Swedish design studio Tomorrow Machine created a series of biodegradable food packaging called This Too Shall Pass. Anna Glansén explained the project in an interview with Matters Journal.
Ok, so generally, “This Too Shall Pass” is a series of food packages where the package and its contents are working in symbiosis. In this project, we asked ourselves how packaging can be made in the near future using technology that is available today.
The smoothie’s package consists only of agar-agar seaweed and water. To open it you pick the top and the package will wither at the same rate as the smoothie. It is made for drinks that have a short life span and needs to be refrigerated. For example, fresh juice, smoothies and cream. The packaging reacts to its environment so you could, just by looking at the package, see if it has been exposed to excessive heat during transport.
The rice package is made of biodegradable beeswax. To open it you peel it like an orange. The package is designed to contain dry goods such as grains and rice.
The oil package is made of caramelised sugar, coated with wax. To open it you crack it like an egg. When the material is cracked the wax no longer protects the sugar and the package melts when it comes in contact with water. This package is made for oil-based food.
(via @pieratt)



Stay Connected