The Beginning of Recorded Sound
Centuries of Sound is a podcast that creates mixtapes by year. So far, that’s pretty standard. The main difference is that CoS’s mixtapes begin in 1853.
That’s as early as we’ve been able to recover recorded audio, mostly from technology that did not work particularly well at the time. The technology of the 1850s recorded sound, but couldn’t reliably reproduce it.
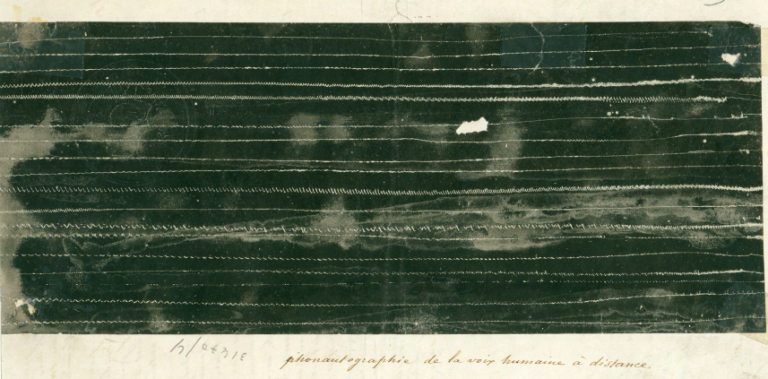
The real start date for us is nearly a quarter of a century [before Thomas Edison], in the studio of French printer and bookseller Édouard-Léon Scott de Martinville. The year was 1853 or 1854, and he was working on engravings for a physiology textbook, in particular a diagram of the internal workings of the human ear. What if, he thought, we could photograph sounds in the way we do images? (photography was a quarter-century old at this point) He began to sketch a device, a way of mimicking the inner workings of the human ear in order to make lines on a piece of paper.
I cover a plate of glass with an exceedingly thin stratum of lampblack. Above I fix an acoustic trumpet with a membrane the diameter of a five franc coin at its small end—the physiological tympanum (eardrum). At its center I affix a stylus—a boar’s bristle a centimeter or more in length, fine but suitably rigid. I carefully adjust the trumpet so the stylus barely grazes the lampblack. Then, as the glass plate slides horizontally in a well formed groove at a speed of one meter per second, one speaks in the vicinity of the trumpet’s opening, causing the membranes to vibrate and the stylus to trace figures.
Firstsounds.org did the most work in deciphering these early paper recordings, and that story is well told by the radio show Studio 360.
It even has a perfect name, what these people do: archeophony.
Here, then, is Centuries of Sound’s mix of all the recorded audio up to 1860 that they’ve been able to recreate from those early, not-at-the-time-reproducible pre-Edison audio signal recordings.
I wish I had known about this when I was still writing my dissertation (which was, in part, on paper and multimedia in the 1900s). It would have made many things much easier.





Stay Connected